
COLLECT EVIDENCE
Use your Science Journal to
record the evidence you collect as
you complete the readings and
activities in this lesson.
INVESTIGATE
GO ONLINE
to find these activities and more resources.
Virtual Investigation: Electron Configuration
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information on
the patterns
present in the periodic
table that translate into patterns of electron states.
Laboratory: Electron Charge-to-Mass Ratio
Analyze and interpret data
to determine the
proportion
of charge to mass for an electron.
Disciplinary Core Ideas
Crosscutting Concepts
Science & Engineering Practices
3D THINKING
C
C
C
S
E
P
D
C
I
Ground-State Electron Configuration
The arrangement of electrons in an atom is called the atom’s
electron configuration.
Because low-energy systems are more stable than high-energy systems, electrons in an
atom tend to assume the arrangement that gives the atom the lowest energy possible.
The most stable, lowest-energy arrangement of the electrons is called the element’s
ground-state electron configuration.
Three rules, or principles—the aufbau
principle, the Pauli exclusion
principle, and Hund’s rule—define
how electrons can be arranged in an
atom’s orbitals.
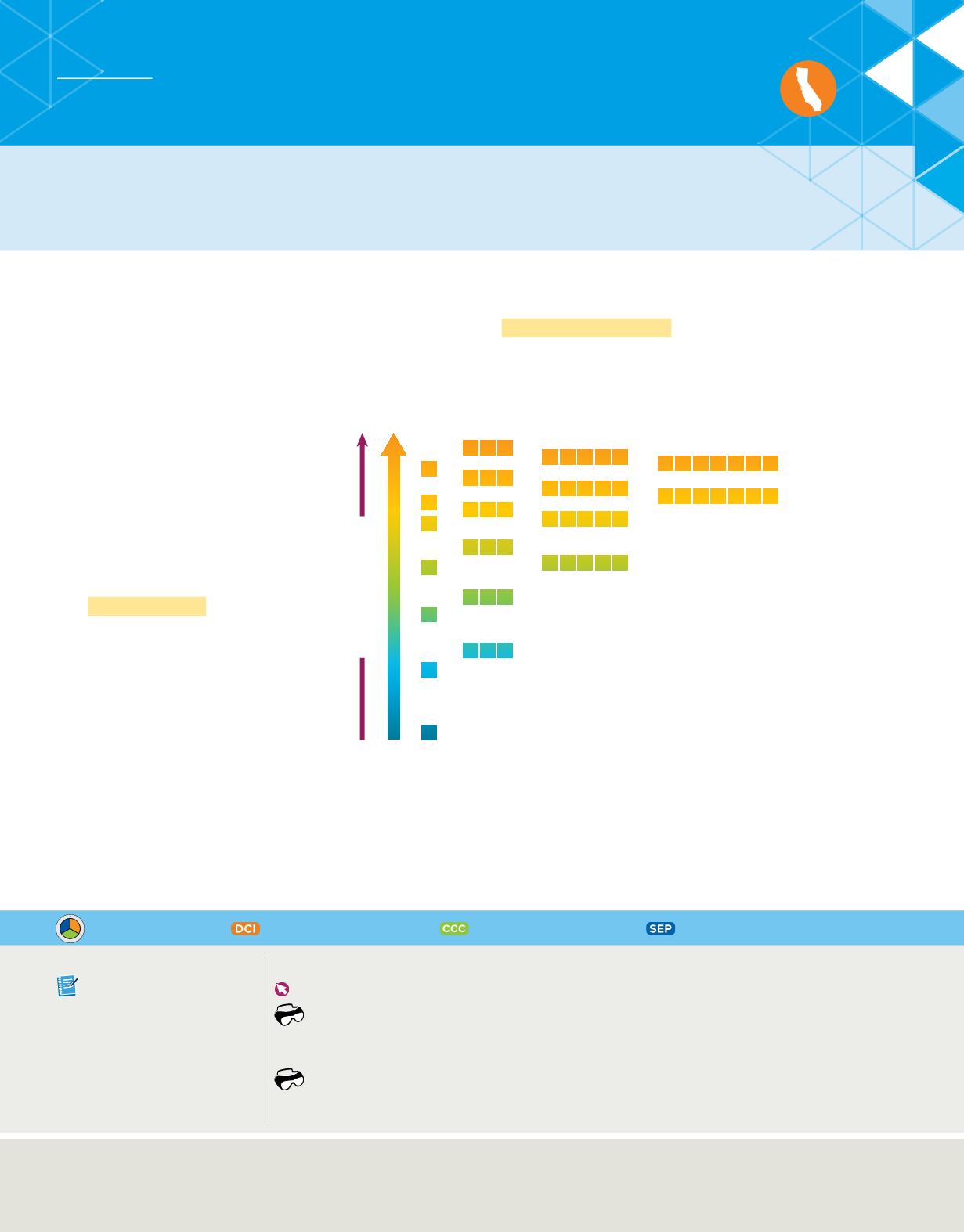
The aufbau principle
The
aufbau principle
states that each
electron occupies the lowest energy
orbital available. Therefore, your first
step in determining an element’s
ground-state electron configuration is
learning the sequence of atomic
orbitals from lowest energy to highest
energy. This sequence, known as an
aufbau diagram, is shown in
Figure 18
.
In the diagram, each box represents
an atomic orbital.
FOCUS QUESTION
How are electrons arranged in atoms?
LESSON 3
ELECTRON CONFIGURATION
C05_030A
Orbital filling sequence
Increasing energy
3d
5d
6d
4d
5f
4f
2p
4p
3p
6p
7p
5p
1s
4s
3s
6s
7s
5s
2s
Figure 18
The aufbau diagram shows the energy of each sublevel
relative to the energy of other sublevels.
Determine
Which sublevel has the greater energy, 4d or 5p?
126
Module 4 • Electrons in Atoms









