
Valence Electrons
Only certain electrons, called valence electrons, determine the chemical properties of an
element.
Valence electrons
are defined as electrons in the atom’s outermost orbitals—
generally those orbitals associated with the atom’s highest principal energy level. For
example, a sulfur atom contains 16 electrons, only six of which occupy the outermost 3s
and 3p orbitals, as shown by sulfur’s electron configuration, [Ne]3s
2
3p
4
. Sulfur has six
valence electrons. Similarly, although a cesium atom has 55 electrons, it has just one
valence electron, the 6s electron shown in cesium’s electron configuration, [Xe]6s
1
.
Electron-dot structures
Because valence electrons are involved in forming chemical bonds, chemists often
represent them visually using a
simple shorthand method, called
electron-dot structure. An atom’s
electron-dot structure
consists of the
element’s symbol, which represents
the atomic nucleus and inner-level
electrons, surrounded by dots
representing all of the atom’s valence
electrons. In writing an atom’s
electron-dot structure, dots repre-
senting valence electrons are placed
one at a time on the four sides of the
symbol (they may be placed in any
sequence) and then paired up until
all are shown.
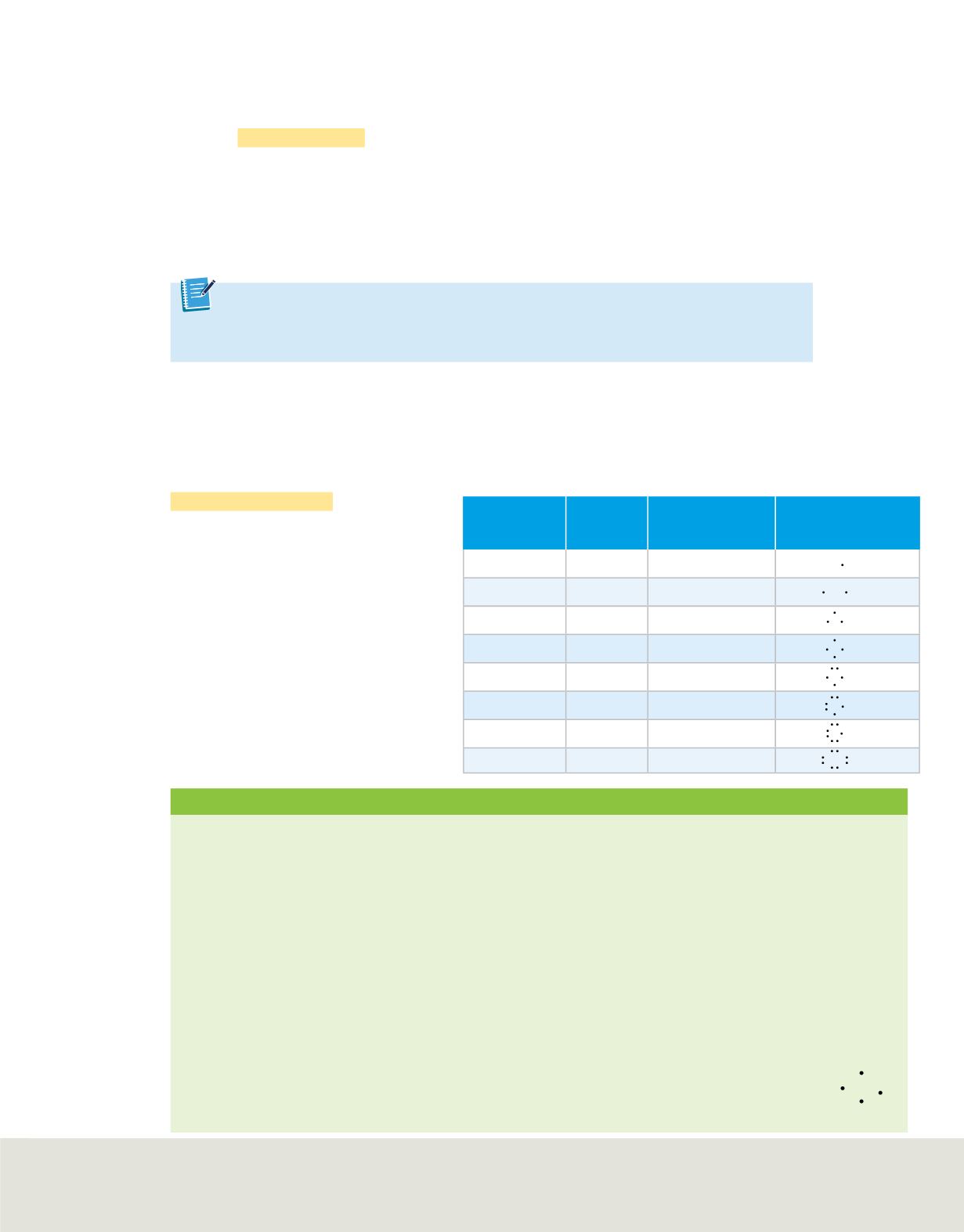
Table 6
shows exam-
ples for the second period.
Table 6
Electron Configurations and Dot
Structures
Element
Atomic
Number
Electron
Configuration
Electron-Dot
Structure
Lithium
3
1s
2
2s
1
Beryllium
4
1s
2
2s
2
Boron
5
1s
2
2s
2
2p
1
Carbon
6
1s
2
2s
2
2p
2
Nitrogen
7
1s
2
2s
2
2p
3
Oxygen
8
1s
2
2s
2
2p
4
Fluorine
9
1s
2
2s
2
2p
5
Neon
10
1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
C05_036A
Li
Be
B
C
N
O
F
Ne
i
EXAMPLE
Problem 3
ELECTRON-DOT STRUCTURES
Some toothpastes contain stannous fluoride, a compound of tin
and fluorine. What is tin’s electron-dot structure?
1
ANALYZE THE PROBLEM
Consult the periodic table to determine the total number of electrons in a tin atom. Write out
tin’s electron configuration, and determine its number of valence electrons. Then use the rules
for electron-dot structures to draw the electron-dot structure for tin.
2
SOLVE FOR THE UNKNOWN
Tin has an atomic number of 50. Thus, a tin atom has 50 electrons.
[Kr]5s
2
4d
10
5p
2
The two 5s and the two 5p electrons (the electrons in the orbitals related to the atom’s
highest principal energy level) represent tin’s four valence electrons. Draw the four valence
electrons around tin’s chemical symbol (Sn) to show tin’s electron-dot structure.
Write out tin’s electron configuration using noble-
gas notation. The closest noble gas is Kr.
C05_037A
Sn
Get It?
Cite Evidence
How do the properties of electrons influence the properties of
elements?
Lesson 3 • Electron Configuration
131









