
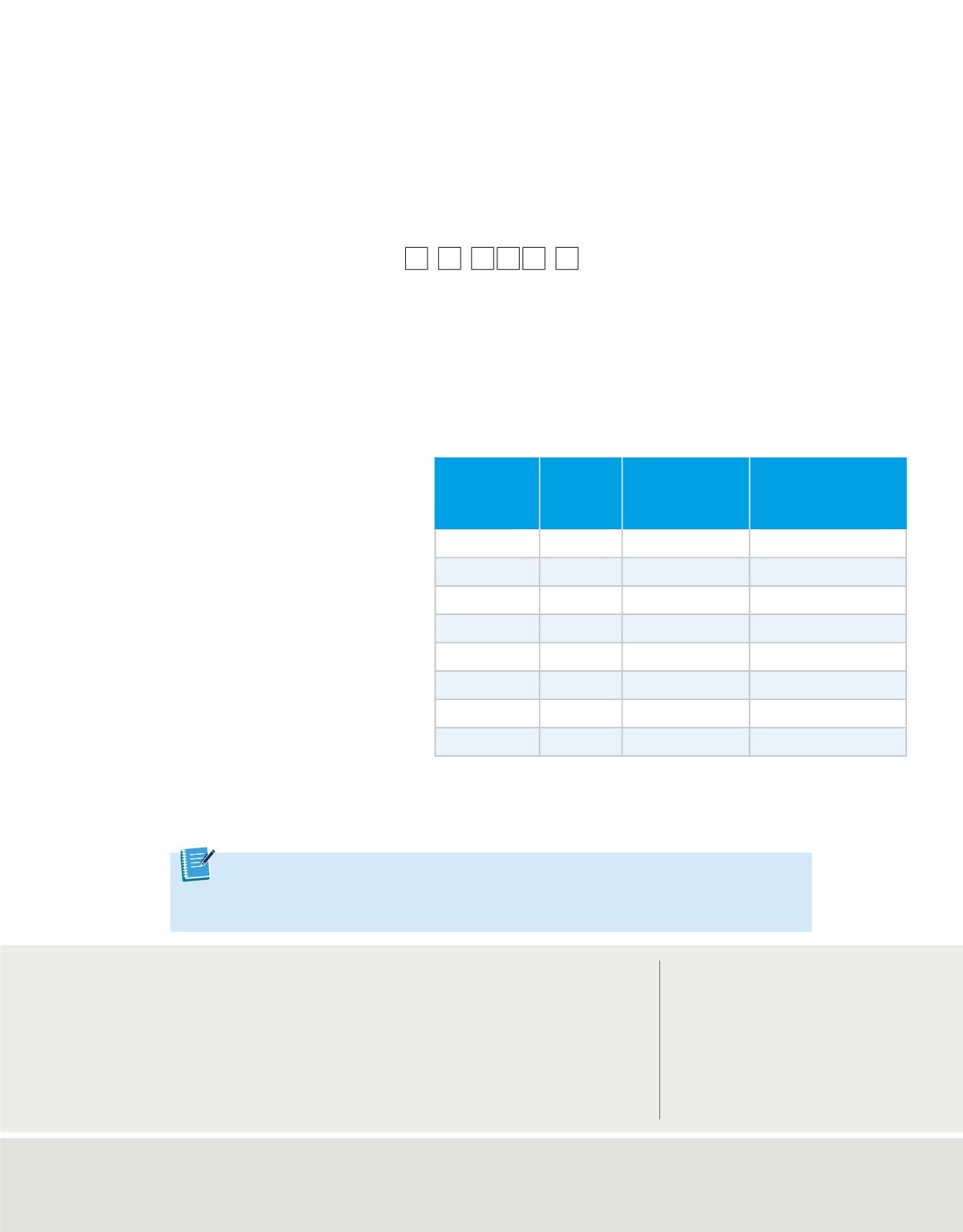
Note that the electron configuration notation does not usually show the orbital
distributions of electrons related to a sublevel. It is understood that a designation
such as nitrogen’s 2p
3
represents the orbital occupancy 2p
x
1
2p
y
1
2p
z
1
.
For sodium, the first ten electrons occupy 1s, 2s, and 2p orbitals. Then, according to
the aufbau sequence, the eleventh electron occupies the 3s orbital. The electron
configuration notation and orbital diagram for sodium are written as follows.
C05_034A
2s
→
→
3s
1s
→
→
2p
→
→
→
→
→
→
→
1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
1
Noble-gas notation
Noble gases are the elements in the last column of the periodic
table. Their outermost energy levels are full, and they are unusually stable. Noble-gas
notation uses bracketed symbols to represent the electron configurations of noble gases.
For example, [He] represents the electron configuration for helium, 1s
2
, and [Ne]
represents the electron configuration for neon, 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
.
Compare the electron configura-
tion for neon with sodium’s
configuration above. Note that
the inner-level configuration for
sodium is identical to the elec-
tron configuration for neon.
Using noble-gas notation, sodi-
um’s electron configuration can
be shortened to the form [Ne]3s
1
.
The electron configuration for an
element can be represented using
the noble-gas notation for the
noble gas in the previous period
and the electron configuration
for the additional orbitals being
filled. The complete and abbrevi-
ated (using noble-gas notation) electron configurations of the period 3
elements are shown in
Table 5.
Get It?
Explain
how to write the noble-gas notation for an element. What is the noble-gas
notation for calcium?
Table 5
Electron Configurations for Elements 11–18
Element
Atomic
Number
Complete
Electron
Configuration
Electron
Configuration
Using Noble Gas
Sodium
11
1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
1
[Ne]3s
1
Magnesium 12
1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
[Ne]3s
2
Aluminum 13
1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
1
[Ne]3s
2
3p
1
Silicon
14 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
2
[Ne]3s
2
3p
2
Phosphorus
15 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
3
[Ne]3s
2
3p
3
Sulfur
16 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
4
[Ne]3s
2
3p
4
Chlorine
17
1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
5
[Ne]3s
2
3p
5
Argon
18 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6
[Ne]3s
2
3p
6
or [Ar]
SCIENCE USAGE V. COMMON USAGE
period
Science usage:
a horizontal row of elements in the current periodic table
There are seven periods in the current periodic table
.
Common usage:
an interval of time determined by some recurring phenomenon
The period of Earth’s orbit is one year
.
WORD ORIGIN
aufbau
comes from the German word
aufbauen
, which means to
build up
or
arrange
Lesson 3 • Electron Configuration
129









