
COLLECT EVIDENCE
Use your Science Journal to
record the evidence you collect as
you complete the readings and
activities in this lesson.
INVESTIGATE
GO ONLINE
to find these activities and more resources.
Laboratory: The Photoelectric Effect
Use mathematical and computational thinking to
observe patterns
in the stability and
instability of physical systems.
Inquiry into Chemistry: Design Atomic Models
Plan and carry out an investigation to
create a model
of the charged subsections
of an atom.
Disciplinary Core Ideas
Crosscutting Concepts
Science & Engineering Practices
3D THINKING
C
C
C
S
E
P
D
C
I
Bohr’s Model of the Atom
The dual wave-particle model of light accounted for several previously unexplainable
phenomena, but scientists still did not understand the relationships among atomic
structure, electrons, and atomic emission spectra. Recall that hydrogen’s atomic
emission spectrum is discontinuous; that is, it is made up of only certain frequencies of
light. Why are the atomic emission spectra of elements discontinuous rather than
continuous? Niels Bohr, a Danish physicist working in Rutherford’s laboratory in 1913,
proposed a quantum model for the hydrogen atom that seemed to answer this question.
Bohr’s model also correctly predicted the frequencies of the lines in hydrogen’s atomic
emission spectrum.
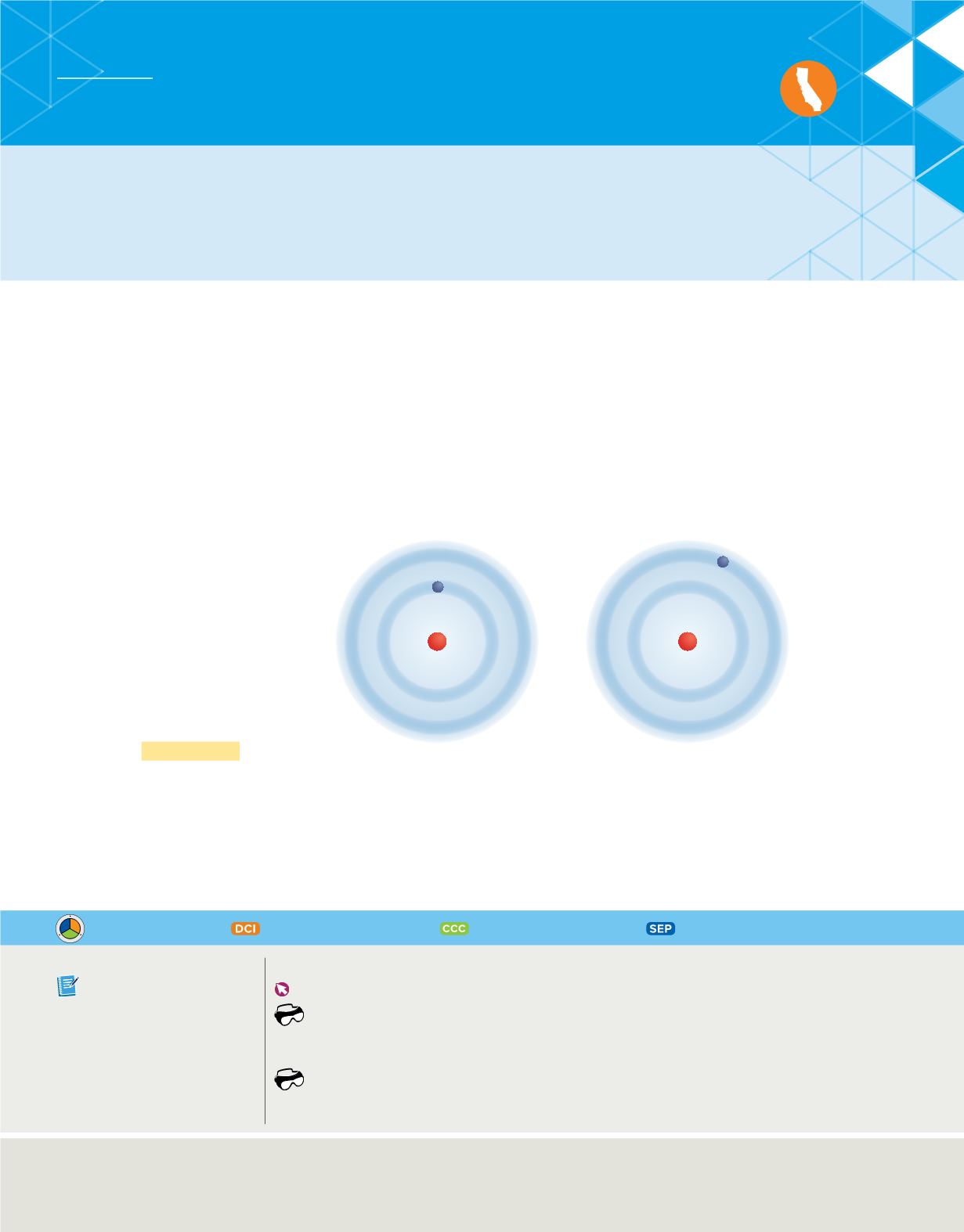
Energy states of hydrogen
Building on Planck’s and
Einstein’s concepts of quantized
energy, Bohr proposed that the
hydrogen atom has only certain
allowable energy states, as
illustrated in
Figure 10
. The lowest
allowable energy state of an atom
is called its
ground state.
When an
atom gains energy, it is said to be
in an excited state.
FOCUS QUESTION
Why does every element produce a unique atomic
emission spectrum?
LESSON 2
QUANTUM THEORY AND THE ATOM
C05_017A
Nucleus
Ground state
Excited state
Electron
Nucleus
Electron
Figure 10
The figure shows an atom that has one electron. Note that the
illustration is not to scale. In its ground state, the electron is associated with
the lowest energy level. When the atom is in an excited state, the electron is
associated with a higher energy level.
116
Module 4 • Electrons in Atoms









