
C04_012A
Voltage source
Opening
connected to
a vacuum pump
Anode (
+
)
Tube
Cathode ( )
+
© Andrew Dunn/Alamy
You might think that because atoms are so small, there would
be no way to see them. However, an instrument called the
scanning tunneling microscope (STM) allows individual atoms
to be seen. An STM works as follows: a fine point is moved
above a sample and the interaction of the point with the
superficial atoms is recorded electronically.
Figure 5
illustrates
how individual atoms look when observed with an STM.
Scientists are now able to move individual atoms around to
form shapes, patterns, and even simple machines. This capability
has led to the exciting new field of nanotechnology. The
promise of nanotechnology is molecular manufacturing—the
atom-by-atom building of machines the size of molecules.
The Electron
Once scientists were convinced of the existence of atoms, a new set of questions emerged.
What is an atom like? Is the composition of an atom uniform throughout, or is it composed
of still-smaller particles? Although many scientists researched the atom in the 1800s, it was
not until almost 1900 that some of these questions were answered. The development of
new technologies allowed scientists to develop models that were used to simulate systems
to determine interactions within and between systems at different scales.
The cathode-ray tube
As scientists tried to unravel the atom, they began to make connections between matter
and electric charge. Scientist learned, through experimentation, using models to simu-
late systems, that the structure and interactions of matter are determined by electrical
forces. With the help of the newly invented vacuum pump, they passed electricity
through glass tubes from which most of the air had been removed. Such tubes are called
cathode-ray tubes and were invented and investigated by scientists from 1869–1875.
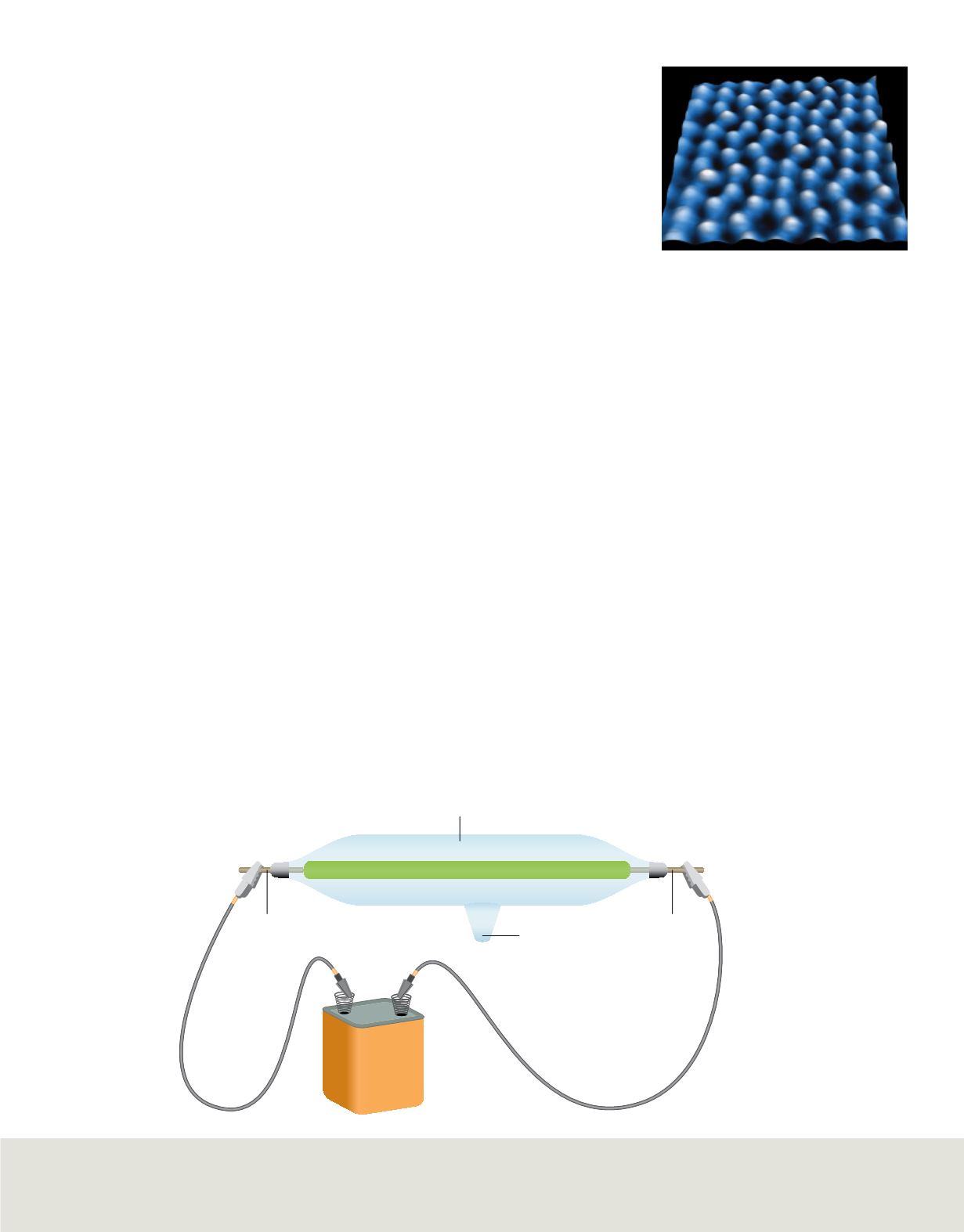
A typical cathode-ray tube used by researchers for studying the relationship between mass
and charge is illustrated in
Figure 6
. Note that metal electrodes are located at opposite
ends of the tube. The electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery is called
the cathode, and the electrode connected to the positive terminal is called the anode.
Figure 6
A cathode-ray
tube is a tube with an anode
at one end and a cathode at
the other end. When a
voltage is applied, electricity
travels from the cathode to
the anode.
Figure 5
This image, recorded with an
STM, shows the individual atoms of a
fatty acid on a graphite surface. The false
colors were added later on to improve
the contrast between each atom.
Lesson 2 • Defining the Atom
83









