
C04_008A
Atoms of Element A
Total mass
=
4(Mass A)
Atoms of Element B
Total mass
=
8(Mass B)
Compound composed
of Elements A and B
Total mass
=
4(Mass A)
+
8(Mass B)
+
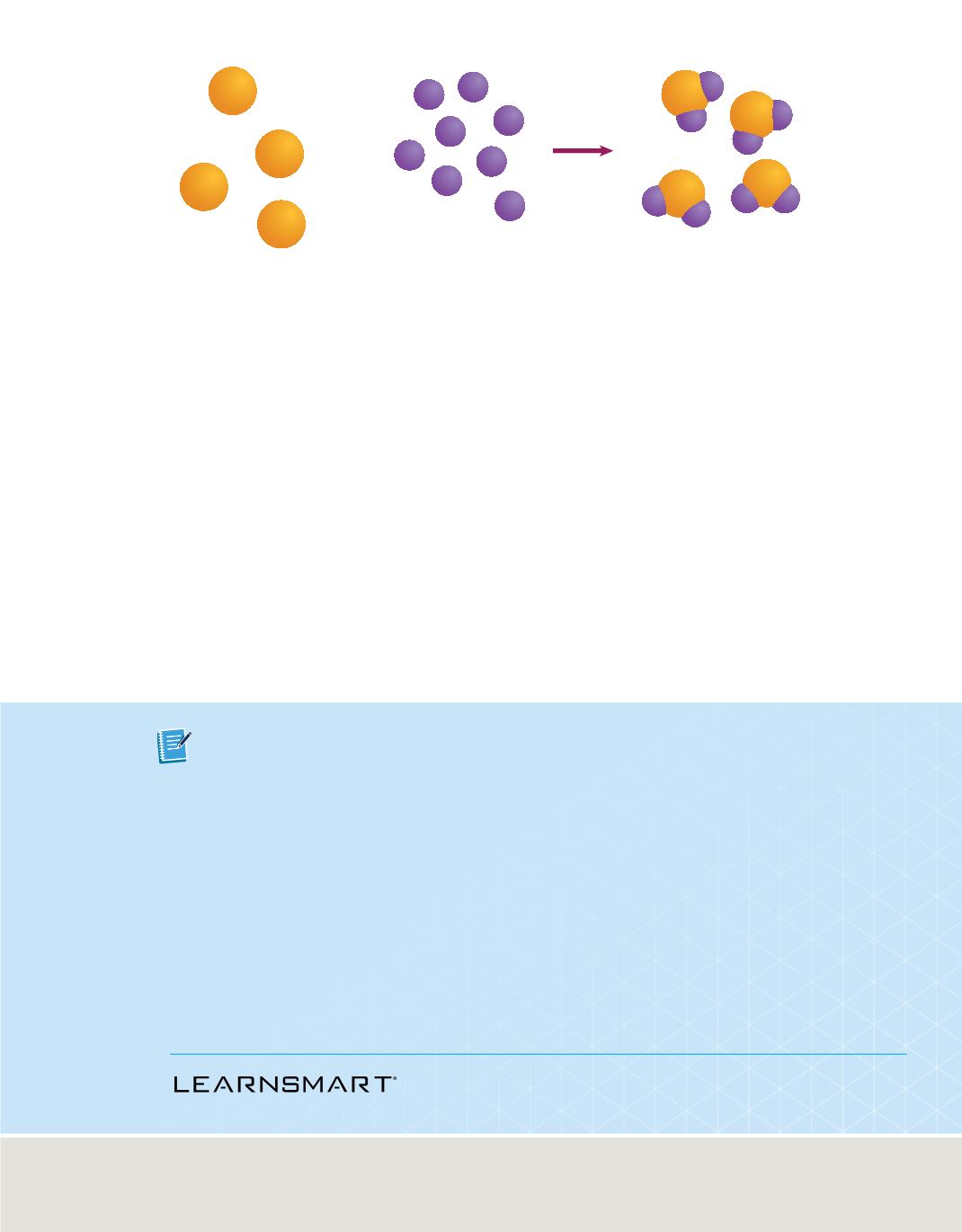
Figure 3
When atoms of two or more elements combine to form a compound, the number of atoms of each
element is conserved. Thus, the mass is conserved as well.
Conservation of mass
The law of conservation of mass states that mass is conserved in any process. Dalton’s
atomic theory explains that the conservation of mass in chemical reactions is the result
of the rearrangement of atoms during the reaction. They are not created or destroyed.
The formation of a compound by combining elements is shown in
Figure 3.
Notice that
the mass ratio for the compound consists of 1 atom of element A and 2 atoms of
element B, a 1:2 ratio. The total number of atoms of each element is the same before
and after the reaction.
Dalton’s convincing experimental evidence and clear explanation of the composition of
compounds, and conservation of mass, led to the general acceptance of his atomic
theory. However, not all of Dalton’s theory was accurate. As our undertanding of atoms
evolved, new information was learned, leading to the revision and improvement of
Dalton’s atomic theory by later scientists.
Check Your Progress
Summary
• Democritus was the first person to
propose the existence of atoms.
• According to Democritus, atoms
are solid, homogeneous, and
indivisible.
• Aristotle did not believe in the
existence of atoms.
• Dalton revised the ideas of
Democritus based on the results
of scientific research.
Demonstrate Understanding
1 .
Summarize
how matter was described by many early
Greek philosophers.
2.
Define
atom
using your own words.
3.
Summarize
Dalton’s atomic theory.
4.
Explain
the relationship between Dalton’s atomic theory
and the conservation of mass in chemical reactions.
5.
Design
a concept map that compares and contrasts
how Democritus, Aristotle, and Dalton viewed matter.
Go online to follow your personalized learning path to review, practice,
and reinforce your understanding.
Lesson 1 • Early Ideas About Matter
81









