
C04_022A
Electron cloud
Nucleus containing
protons and neutrons
Summary
• An atom is the smallest particle
of an element that maintains
the properties of that element.
• Electrons have a 1
-
charge,
protons have a 1
+
charge, and
neutrons have no charge.
• An atom consists mostly of
empty space surrounding the
nucleus.
Check Your Progress
Demonstrate Understanding
6.
Describe
the structure of a typical atom. Identify the
location and charge of each subatomic particle.
7.
Compare and contrast
Thomson’s plum pudding
atomic model with Rutherford’s nuclear atomic model.
8.
Describe
the research, including instrumentation,
which led to the conclusion that electrons are nega-
tively charged particles found in all matter.
9.
Compare
the relative charge and mass of each
subatomic particle.
10.
Calculate
What is the difference expressed in
kilograms between the mass of a proton and the
mass of an electron?
Go online to follow your personalized learning path to review, practice,
and reinforce your understanding.
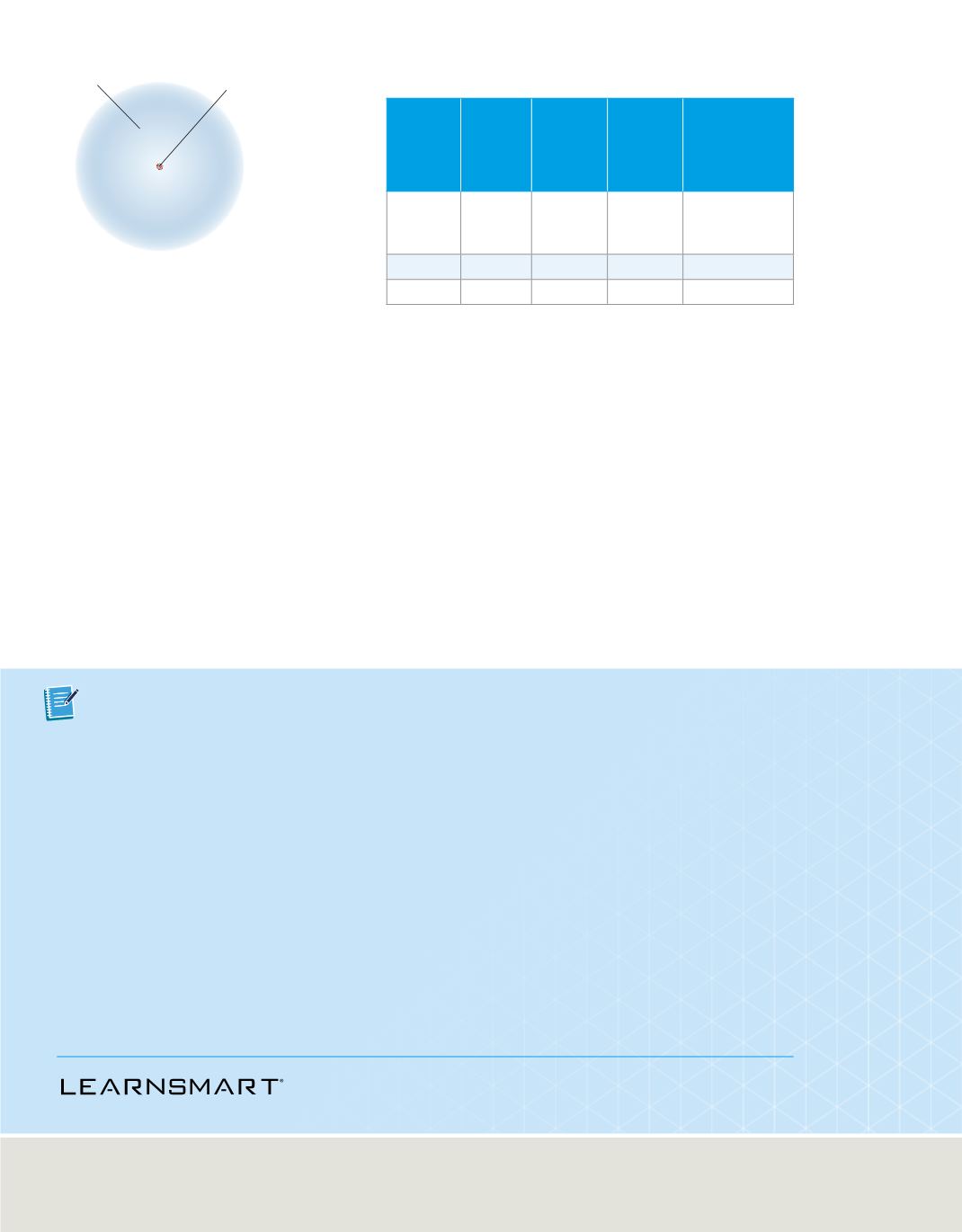
Most of an atom consists of fast-moving electrons traveling through empty space around
the nucleus. The electrons are held within the atom by their attraction to the positively
charged nucleus. The nucleus, which is composed of neutral neutrons (hydrogen’s
single-proton nucleus is an exception) and positively charged protons, contains more
than 99.97% of an atom’s mass. It occupies only about one ten-thousandth of the
volume of the atom. Because an atom is electrically neutral, the number of protons in
the nucleus equals the number of electrons around the nucleus. The typical atom is
shown in
Figure 14
, and the properties of the subatomic particles are summarized in
Table 3.
Scientists have determined that protons and neutrons have their own structures. They
are composed of subatomic particles called quarks. These particles will not be covered
in this textbook because scientists do not yet understand if or how they affect chemical
behavior. Chemical behavior can be explained by considering only an atom’s electrons.
Figure 14
Atoms are composed of a nucleus
containing protons and neutrons, and surrounded
by a cloud of electrons.
Table 3
Properties of Subatomic Particles
Particle Symbol
Relative
Electric
Charge
Relative
Mass
Actual Mass
(g)
Electron e
-
1
-
1 ____ 1840
9.11
×
10
-
28
Proton
p
1
+
1
1.673
×
10
-
24
Neutron n
0
1
1.675
×
10
-
24
90
Module 3 • The Structure of the Atom









