
C04_026A
63
29
Cu
65
29
Cu
Mass number
Atomic number
C04_027A
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
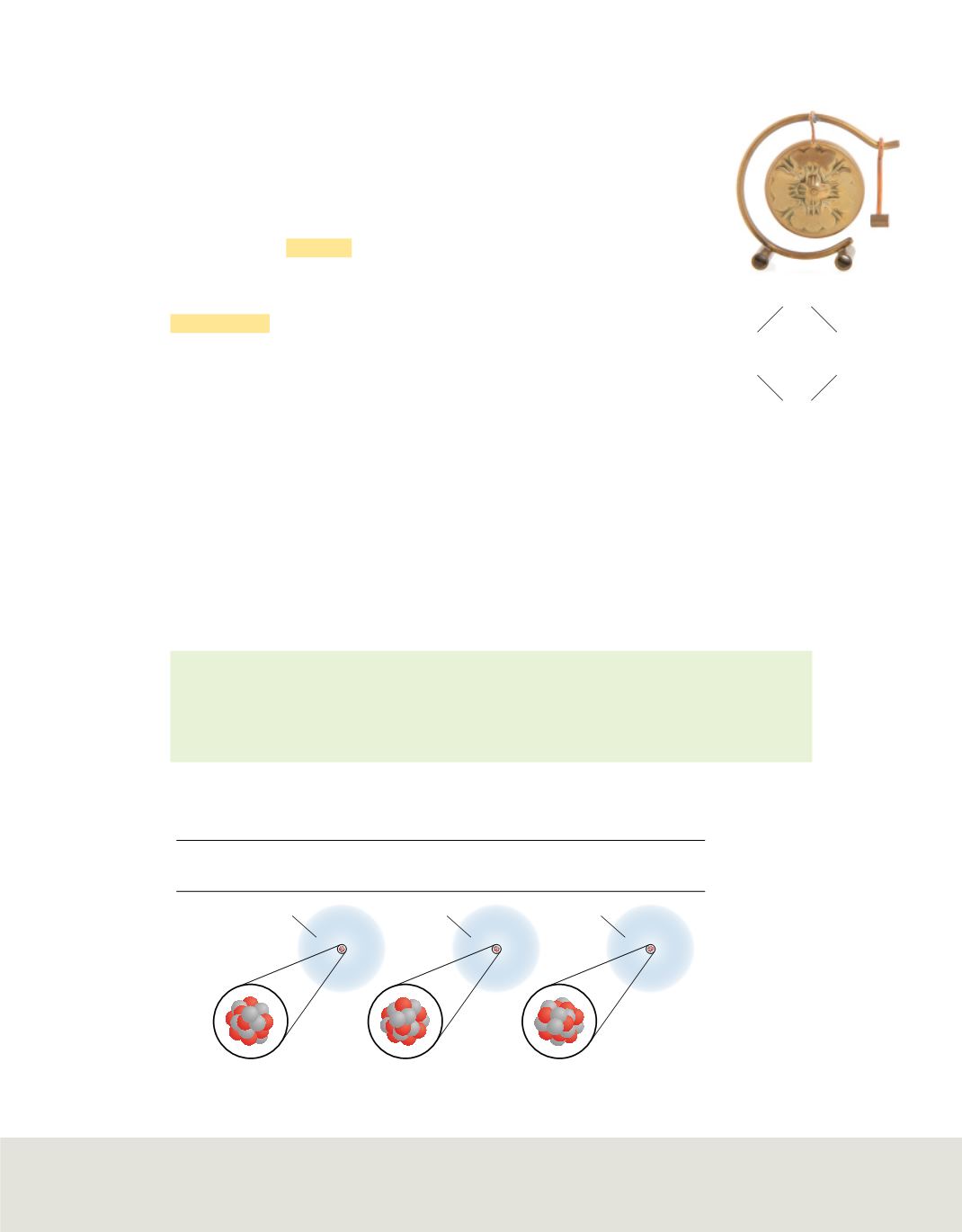
Potassium-39
19
20
19
Potassium-40
19
21
19
Potassium-41
19
22
19
19e
19e
19e
19p
20n
19p
21n
19p
22n
K
39
19
K
40
19
K
41
19
© Martin Wierink/Alamy
Isotopes and Mass Number
All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons,
but the number of neutrons might differ. For example, there are three
types of potassium atoms that occur naturally and all three types contain
19 protons and 19 electrons. However, one type of potassium atom
contains 20 neutrons, another 21 neutrons, and still another 22 neutrons.
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neu-
trons are called
isotopes.
Mass of isotopes
While isotopes that contain more neutrons have a
greater mass, all isotopes of an atom have the same chemical behavior. The
mass number
identifies each isotope of an element and is the sum of the
atomic number (or number of protons) and neutrons in the nucleus.
For example, copper has two isotopes. The isotope with 29 protons and 34
neutrons has a mass number of 63 (29
+
34
=
63), and is called copper-63
(also written
63
Cu or Cu-63). The isotope with 29 protons and
36 neutrons is called copper-65. Chemists often write out isotopes using a
notation shown in
Figure 16.
Natural abundance of isotopes
In nature, most elements are found
as mixtures of isotopes. Usually, the relative abundance of each isotope is
constant. Different sources containing atoms of potassium would have
the same percent composition of potassium isotopes. The three potassium
isotopes are summarized in
Figure 17
.
Mass number
mass number
=
atomic number
+
number of neutrons
The mass number of an atom is the sum of its atomic number and its number of neutrons.
Figure 16
Cu is the
chemical symbol for copper.
Copper, which was used to
make this Chinese gong, is
composed of 69.2%
copper-63 and 30.8%
copper-65.
Figure 17
Potassium has three
naturally occurring isotopes,
potassium-39, potassium-40,
and potassium 41. The table
lists the number of protons,
neutrons, and electrons in each
potassium isotope.
Lesson 3 • How Atoms Differ
93









