
GO ONLINE
to study with your Science Notebook.
Lesson 1
DEVELOPMENT OF THE MODERN PERIODIC TABLE
• periodic law
• group
• period
• representative element
• transition element
• metal
• alkali metal
• alkaline earth metal
• transition metal
• inner transition metal
• lanthanide series
• actinide series
• nonmetal
• halogen
• noble gas
• metalloid
• The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass,
which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by
increasing atomic number.
• The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by
increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their
chemical and physical properties.
• The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and
groups or families (columns); elements with similar properties are
in the same group.
• Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids.
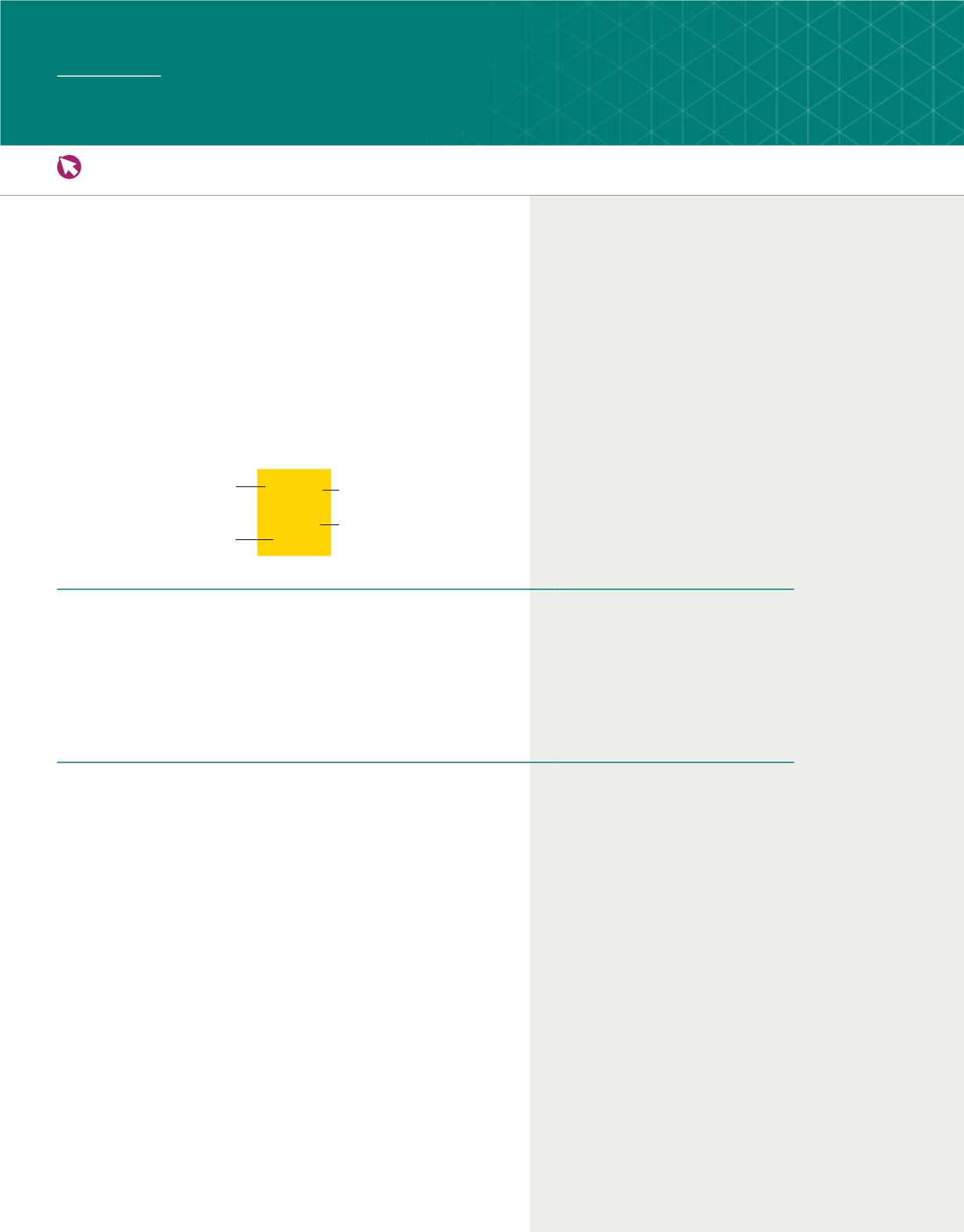
C06_005A
Atomic
number
Element
Oxygen
15.999
Atomic
mass
Symbol
8
O
Lesson 2
CLASSIFICATION OF THE ELEMENTS
• The periodic table has four blocks (s, p, d, f).
• Elements within a group have similar chemical properties.
• The group number for elements in groups 1 and 2 equals the
element’s number of valence electrons.
• The energy level of an atom’s valence electrons equals its period
number.
Lesson 3
PERIODIC TRENDS
• ion
• ionization energy
• octet rule
• electronegativity
• Atomic and ionic radii decrease from left to right across a period,
and increase as you move down a group.
• Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a
period, and decrease down a group.
• The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to
acquire a full set of eight valence electrons.
• Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a
period, and decreases down a group.
MODULE 5
STUDY GUIDE
162
Module 5 • Study Guide









