
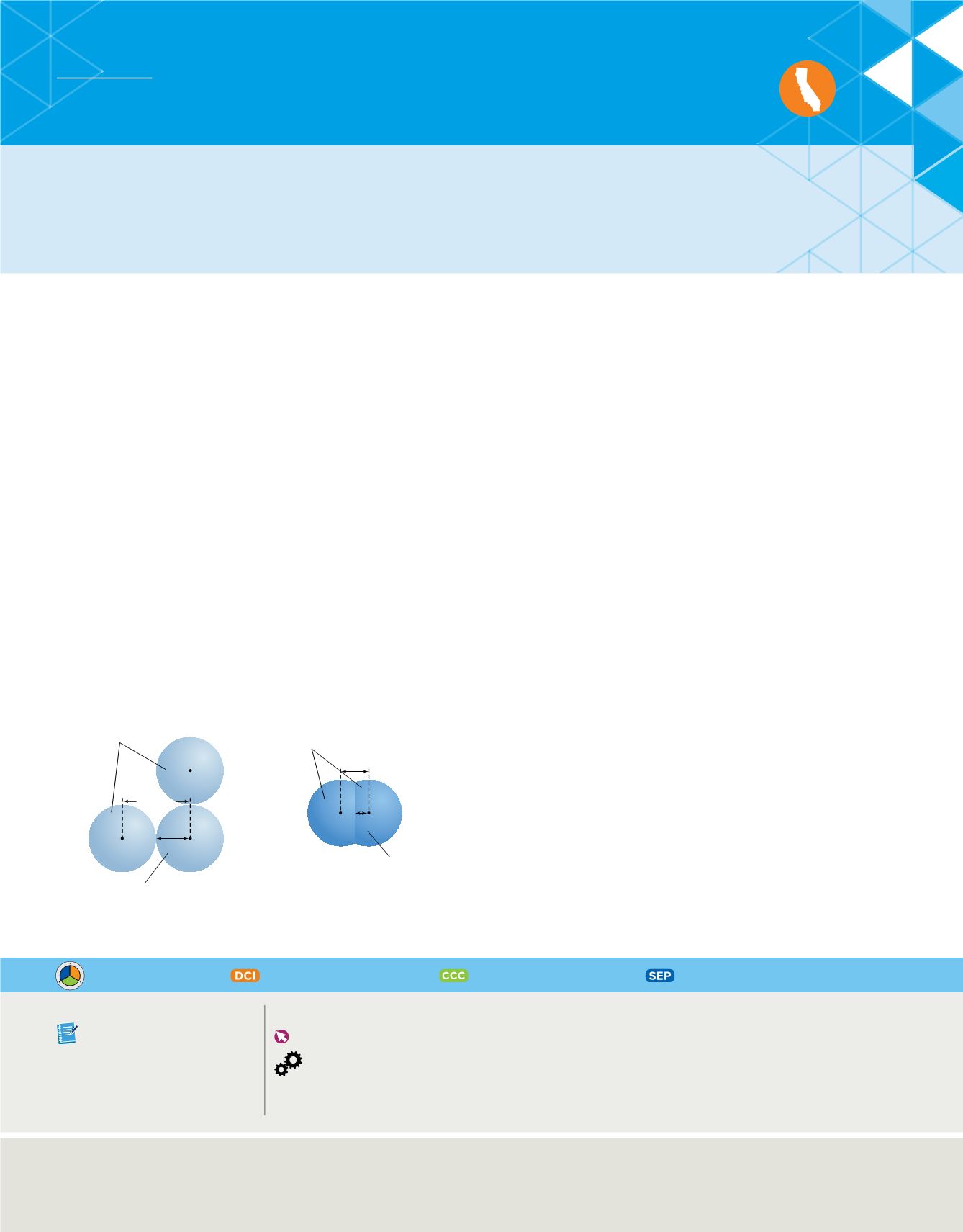
C06_012A
Bonded nonmetal hydrogen
atoms in a molecule
Radius
Radius
Bonded metallic
sodium atoms in
a crystal lattice
186 pm
372 pm
74 pm
37 pm
The radius of a metal atom is one-half
the distance between two adjacent
atoms in the crystal.
The radius of a nonmetal atom is often
determined from a molecule of two
identical atoms.
Atomic Radius
Many properties of the elements tend to change in a predictable way, known as a trend,
as you move across a period or down a group. Atomic size is one such periodic trend.
The sizes of atoms are influenced by electron configuration.
Recall that the electron cloud surrounding a nucleus does not have a clearly defined
edge. The outer limit of an electron cloud is defined as the spherical surface within
which there is a 90% probability of finding an electron. However, this surface does not
exist in a physical way, as the outer surface of a golf ball does. Atomic size is defined by
how closely an atom lies to a neighboring atom. Because the nature of the neighboring
atom can vary from one substance to another, the size of the atom itself also tends to
vary somewhat from substance to substance.
For metals such as sodium, the atomic radius is defined as half the distance between adja-
cent nuclei in a crystal of the element, as shown in
Figure 11
. For elements that commonly
occur as molecules, such as many nonmetals, the atomic radius is defined as half the
distance between nuclei of identical atoms that are chemically bonded together. The atomic
radius of a nonmetal diatomic hydrogen molecule (H
2
) is shown in
Figure 11
.
Figure 11
Atomic radii depend on the type
of bonds that atoms form.
FOCUS QUESTION
How can you use the periodic table to predict an
element’s properties?
LESSON 3
PERIODIC TRENDS
Disciplinary Core Ideas
Crosscutting Concepts
Science & Engineering Practices
3D THINKING
C
C
C
S
E
P
D
C
I
COLLECT EVIDENCE
Use your Science Journal to
record the evidence you collect as
you complete the readings and
activities in this lesson.
INVESTIGATE
GO ONLINE
to find these activities and more resources.
Applying Practice:
Electron Patterns of Atoms
HS-PS1-1.
Use the periodic table as a model to predict
the relative properties of elements
based on patterns
of electrons in the outermost energy level of atoms.
152
Module 5 • The Periodic Table and Periodic Law









