
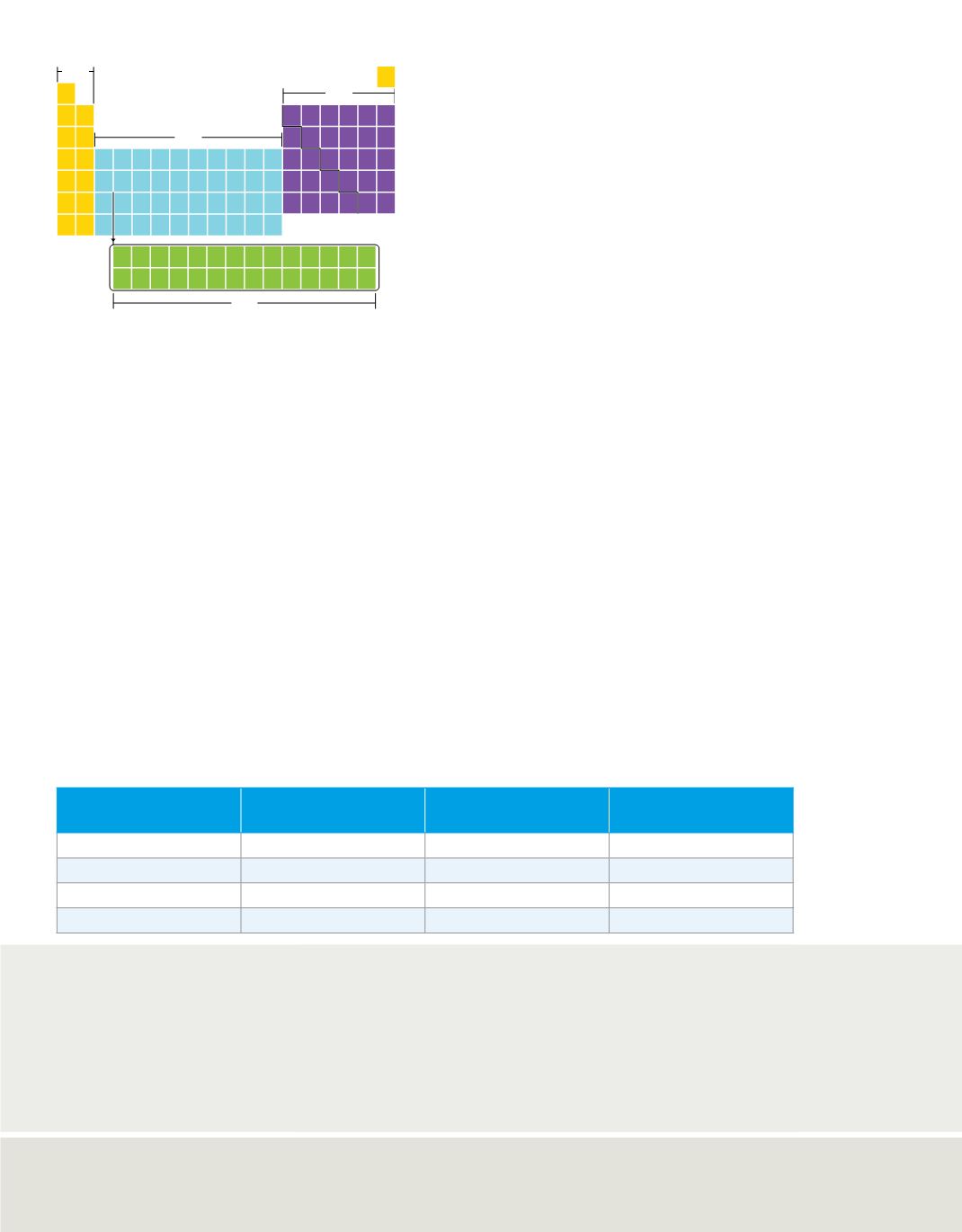
C06_010A
s block
p block
d block
f block
Figure 9
The periodic table is divided into
four blocks—s, p, d, and f.
Analyze
What is the relationship between
the maximum number of electrons an
energy sublevel can hold and the number of
columns in that block on the diagram?
Table 4
Noble Gas Electron Configuration
Period
Principal Energy Level
Element
Electron
Configuration
1
n
=
1
helium
1s
2
2
n
=
2
neon
[He]2s2
2
p
6
3
n
=
3
argon
[Ne]3s
2
3p
6
4
n
=
4
krypton
[Ar]4s
2
3d
10
4p
6
p-Block elements
After the s sublevel is filled, the valence electrons next occupy the p sublevel. The p-block is
comprised of groups 13 through 18 and contains elements with filled or partially filled p
orbitals. There are no p-block elements in period 1 because the p sublevel does not exist for
the first principal energy level (n
=
1). The first p-block element is boron (B), which is in the
second period. The p-block spans six groups because the three p orbitals can hold a maxi-
mum of six electrons.
The group 18 elements, which are called the noble gases, are unique members of the
p-block. The atoms of these elements are so stable that they undergo virtually no chemical
reactions. The electron configurations of the first four noble gas elements are shown in
Table 4
. Here, both the s and p orbitals corresponding to the period’s principal energy level
are completely filled. This arrangement of electrons results in an unusually stable atomic
structure. Together, the s- and p-blocks comprise the representative elements.
d-Block elements
The d-block contains the transition metals and is the largest of the blocks. With some
exceptions, d-block elements are characterized by a filled outermost s orbital of energy
level n, and filled or partially filled d orbitals of energy level
n
−1.
ACADEMIC VOCABULARY
structure
something made up of more-or-less interdependent elements or parts
Many scientists were involved in the discovery of the structure of the atom.
148
Module 5 • The Periodic Table and Periodic Law









