
C05_010A
10
4
3
×
10
4
3
×
10
2
3
3
×
10
−
2
3
×
10
4
3
×
10
6
3
×
10
8
3
×
10
10
3
×
10
12
3
×
10
14
10
6
10
8
10
10
10
12
10
14
10
16
10
18
10
20
10
22
Frequency (
ν
) in hertz
Gamma rays
Ultraviolet
Infrared
Radio
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Wavelength (
λ
) in meters
Visible light
Microwaves
X rays
Energy/frequency increases
Wavelength increases
Get It?
Explain
how wavelength and frequency of a wave are related.
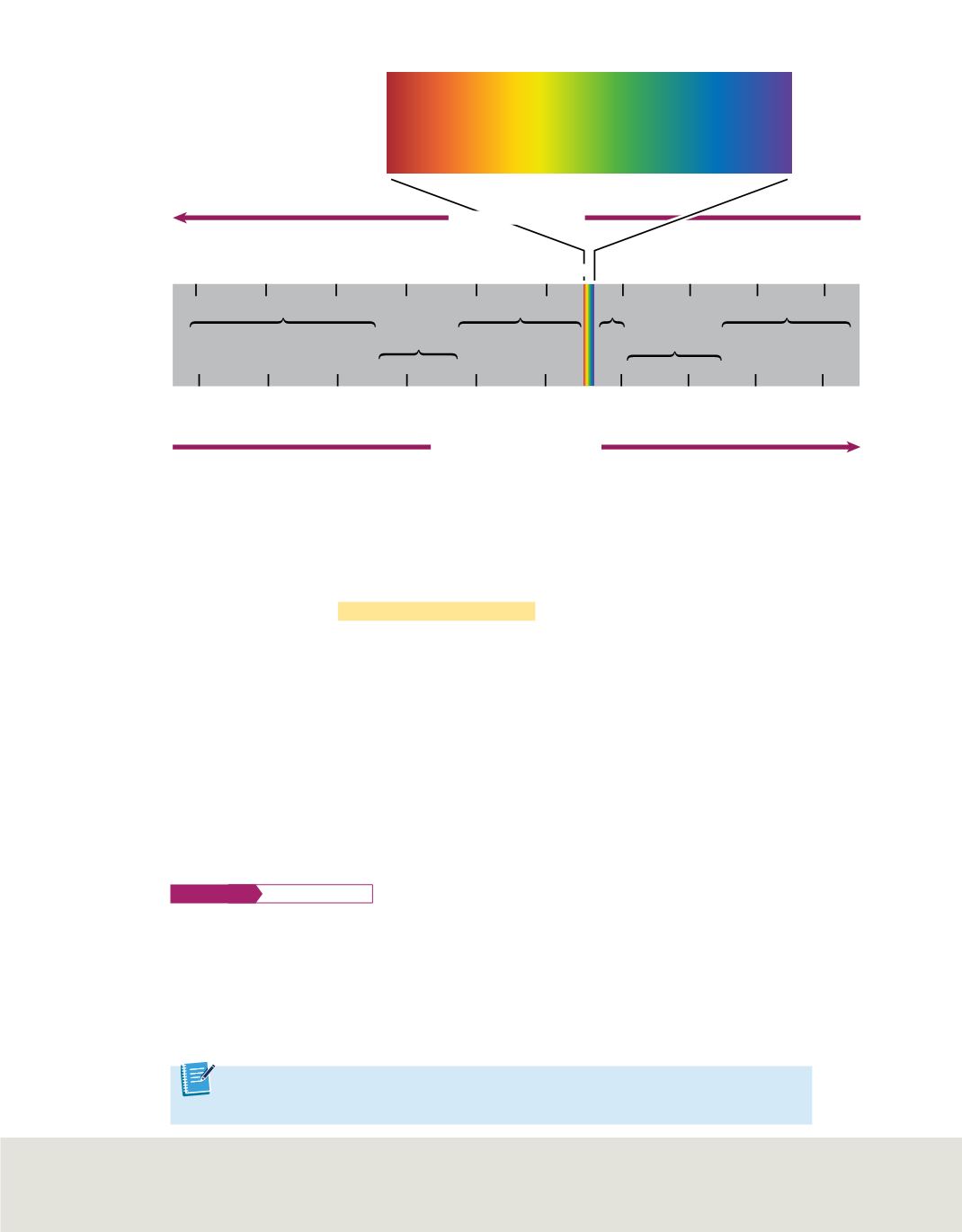
The visible spectrum of light, shown in
Figure 4
, comprises only a small portion of the
complete electromagnetic spectrum. The complete electromagnetic spectrum is illus-
trated in
Figure 5
. The
electromagnetic spectrum,
also called the EM spectrum,
includes all forms of electromagnetic radiation, with the only differences in the types of
radiation being their frequencies and wavelengths.
Note in
Figure 4
that the bend varies with the wavelengths as they pass through the
prism, resulting in the sequence of the colors red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and
violet. In examining the energy of the radiation shown in
Figure 5
, note that energy
increases with increasing frequency. Thus, looking back at
Figure 3
, the violet light, with
its greater frequency, has more energy than the red light. This relationship between
frequency and energy will be explained in the next lesson. The wavelength and frequency
of a wave are related to one another by the speed of travel of the wave, which depends on
the type of wave and the medium through which it is passing. For light waves, you can
use the formula c
= λν
to calculate the wavelength or frequency of any wave.
PHYSICS
Connection
Electromagnetic radiation from diverse origins constantly
bombards us. In addition to the radiation from the Sun, technology such as radio and
TV signals, phone relay stations, lightbulbs, medical X-ray equipment, and particle
accelerators also produce radiation. Natural sources on Earth, such as lightning, natural
radioactivity, and even the glow of fireflies, also contribute. Our knowledge of the
universe is based on electromagnetic radiation emitted by distant objects and detected
with instruments on Earth.
Figure 5
The electromagnetic spectrum covers a wide range of frequencies. The visible-light section of the spectrum
is very narrow. As frequency and energy increase, wavelength decreases.
Lesson 1 • Light and Quantized Energy
109









