
C04_032A
Lead block
Radioactive
source
Hole
Positive plate
Beta
particles
(1 charge)
Alpha
particles
(2
+
charge)
Zinc-sulfide-
coated screen
Gamma rays
(no charge)
Negative plate
+
β
γ
α
Types of Radiation
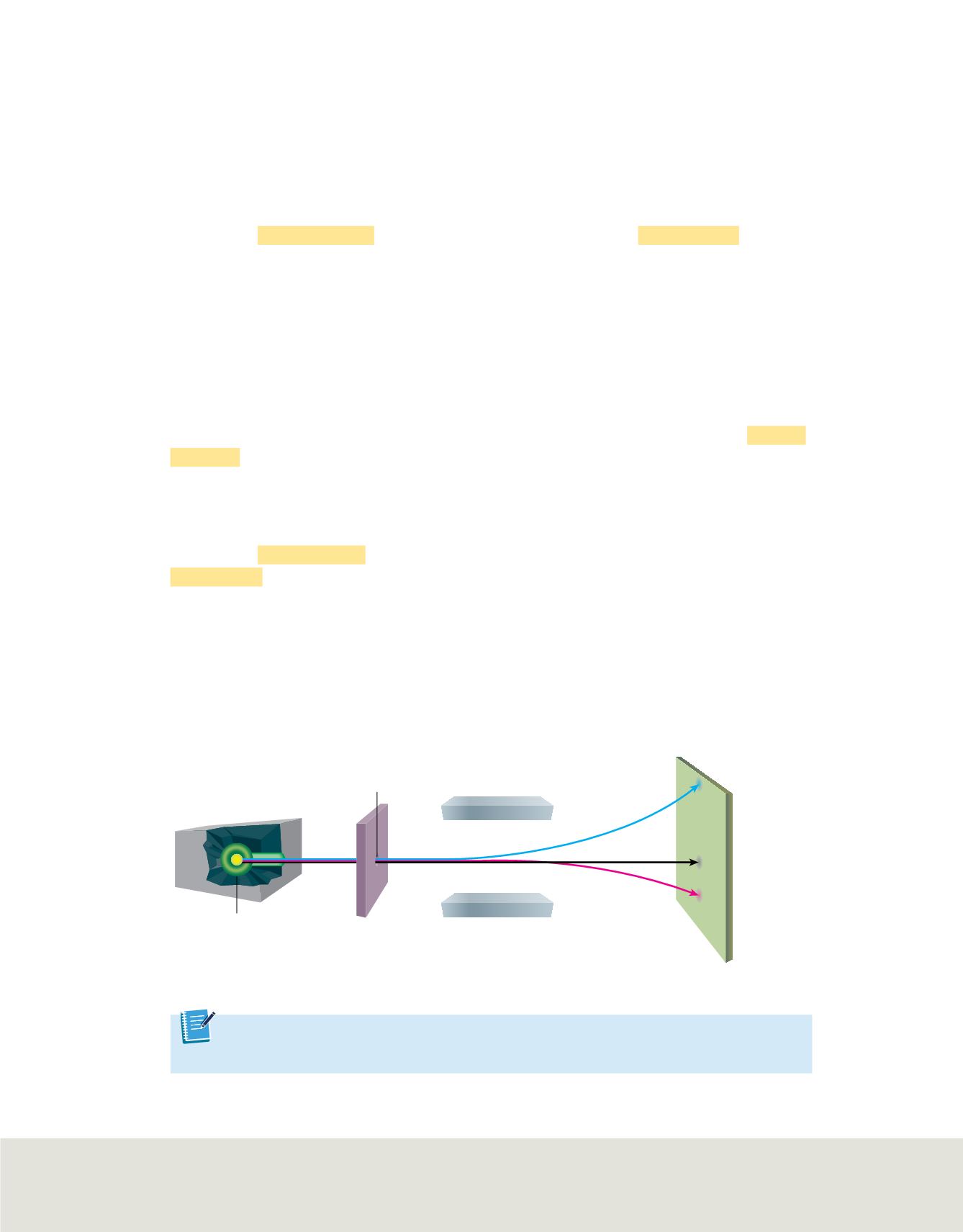
Scientists began researching radioactivity in the late 1800s. By directing radiation from a
radioactive source between two electrically charged plates, scientists were able to identify
three different types of radiation based on their electric charge. As shown in
Figure 21
,
radiation was deflected toward the negative plate, the positive plate, or not at all.
Alpha radiation
The radiation that was deflected toward the negatively charged plate
was named
alpha radiation.
It is made up of alpha particles. An
alpha particle
contains
two protons and two neutrons, and thus has a 2
+
charge, which explains why alpha
particles are attracted to the negatively charged plate as shown in
Figure 21
. An alpha
particle is equivalent to a helium-4 nucleus and is represented by
4
2
He or
α
. The alpha
decay of radioactive radium-226 into radon-222 is shown below.
226
88
Ra
→
222
86
Rn
+
α
radium-226 radon-222 alpha particle
Note that a new element, radon (Rn), is created as a result of the alpha decay of the
unstable radium-226 nucleus. The type of equation shown above is known as a
nuclear
equation.
It shows the atomic numbers and mass numbers of the particles involved.
Note that in a nuclear equation, although elements are not conserved, the total number
of protons plus neutrons is conserved.
Beta radiation
The radiation that was deflected toward the positively charged plate
was named
beta radiation.
This radiation consists of fast-moving beta particles. Each
beta particle
is an electron with a 1– charge. The negative charge of the beta particle
explains why it is attracted to the positively charged plate shown in
Figure 21
. Beta
particles are represented by the symbol
β
or e
–
. The beta decay of carbon-14 into
nitrogen-14 is shown below. The beta decay of unstable carbon-14 results in the
formation of the new element, nitrogen (N).
14
6
C
→
14
7
N
+
β
carbon-14 nitrogen-14 beta particle
Figure 21
An electric
field will deflect
radiation in different
directions, depending
on the electric charge
of the radiation.
Get It?
Compare and contrast
alpha decay and beta decay.
Lesson 4 • Unstable Nuclei and Radioactive Decay
99









