
TinnaPong/Shutterstock.com
Radioactivity
Nuclear reactions
In the late 1890s, scientists noticed that some substances
spontaneously emitted radiation in a process they named
radioactivity.
The rays and
particles emitted by the radioactive material were called
radiation.
Scientists discovered
that radioactive atoms undergo changes that can alter their identities. A reaction that
involves a change in an atom’s nucleus is called a
nuclear reaction.
Prior to this
discovery, it was not known that a reaction could result in the formation of a new
element. Radioactive atoms emit radiation because their nuclei are unstable. Unstable
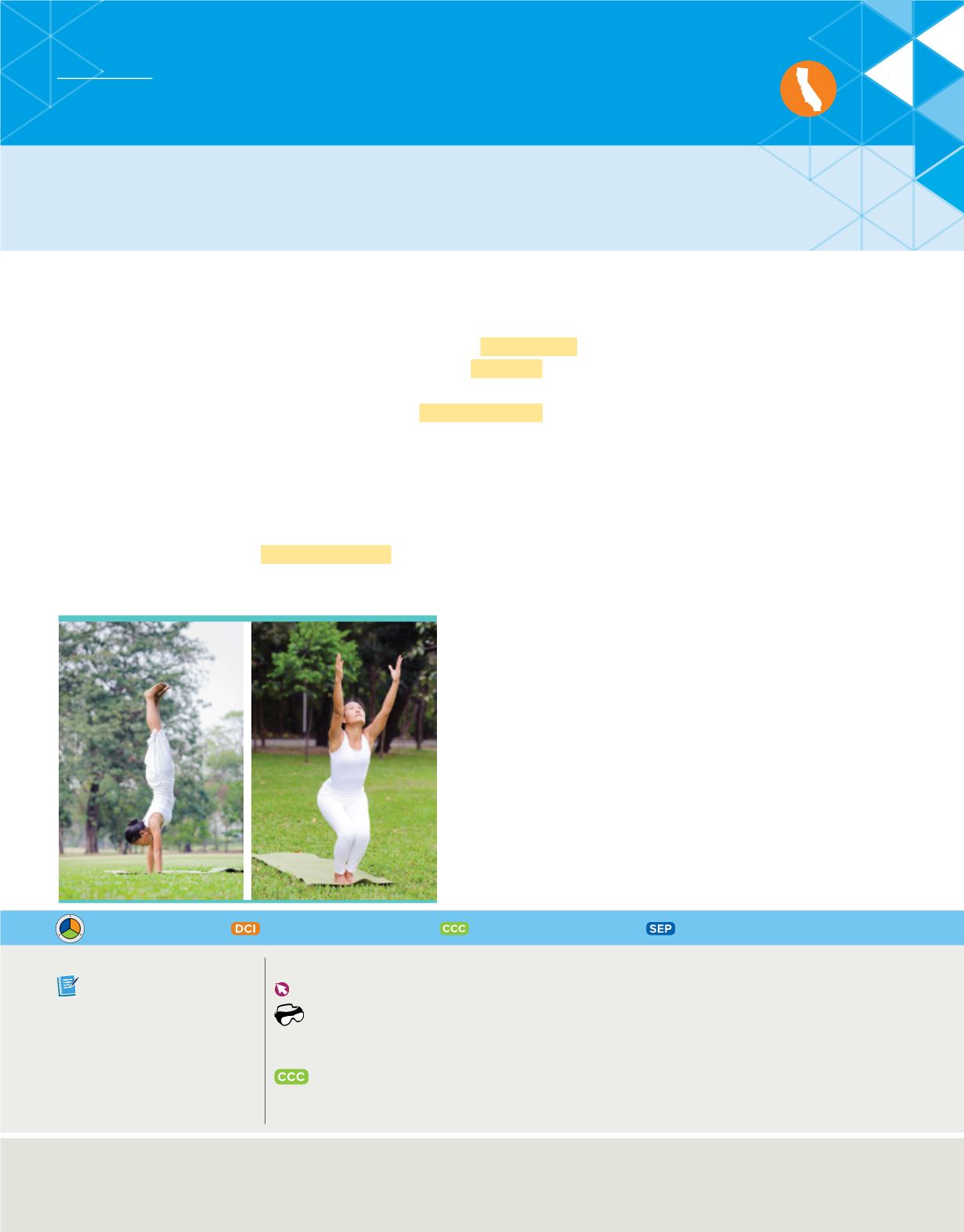
systems, whether they are atoms or people doing handstands, as shown in
Figure 20
,
gain stability by losing energy.
Radioactive decay
Unstable nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation in a
spontaneous process called
radioactive decay.
Unstable atoms undergo radioactive
decay until they form stable atoms, often of a different element. An atom can lose
energy and reach a stable state when emitting radiation.
Figure 20
Being in a handstand
position is an unstable state. Like
unstable atoms, people doing
handstands eventually return to a
more stable state – standing on
their feet – by losing potential
energy.
FOCUS QUESTION
How can atoms change?
LESSON 4
UNSTABLE NUCLEI AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY
Disciplinary Core Ideas
Crosscutting Concepts
Science & Engineering Practices
3D THINKING
C
C
C
S
E
P
D
C
I
COLLECT EVIDENCE
Use your Science Journal to
record the evidence you collect as
you complete the readings and
activities in this lesson.
INVESTIGATE
GO ONLINE
to find these activities and more resources.
Laboratory:
Half-Life of Barium-137m
Construct an explanation
to determine
the
stability and change
of
an atom experiencing
spontaneous radioactive decay.
Identify Crosscutting Concepts
Create a table of the
crosscutting concepts
and fill in examples you find as you read.
98
Module 3 • The Structure of the Atom









