
Noboru Hashimoto/Corbis Historical/Getty Images
Go online to follow your personalized learning path to review, practice,
and reinforce your understanding.
Check Your Progress
Summary
• The elements were first orga-
nized by increasing atomic
mass, which led to inconsisten-
cies. Later, they were organized
by increasing atomic number.
• The periodic law states that
when the elements are
arranged by increasing atomic
number, there is a periodic
repetition of their chemical and
physical properties.
• The periodic table organizes the
elements into periods (rows) and
groups or families (columns);
elements with similar properties
are in the same group.
• Elements are classified as
metals, nonmetals, or
metalloids.
Demonstrate Understanding
1.
Describe
the development of the periodic table.
2.
Sketch
a simplified version of the periodic table, and
indicate the location of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
3.
Describe
the general characteristics of metals, non-
metals, and metalloids.
4.
Identify
each of the following as a representative
element or a transition element.
a. lithium (Li)
c. promethium (Pm)
b. platinum (Pt)
d. carbon (C)
5.
Compare
For each of the given elements, list two
other elements with similar chemical properties.
a. iodine (I) b.
barium (Ba) c.
iron (Fe)
6.
Compare
According to the periodic table, which two
elements have an atomic mass less than twice their
atomic number?
7.
Interpret Data
A company plans to make an electronic
device. They need to use an element that has chemical
behavior similar to that of silicon (Si) and lead (Pb). The
element must have an atomic mass greater than that of
sulfur (S) but less than that of cadmium (Cd). Use the
periodic table to predict which element the company
will use.
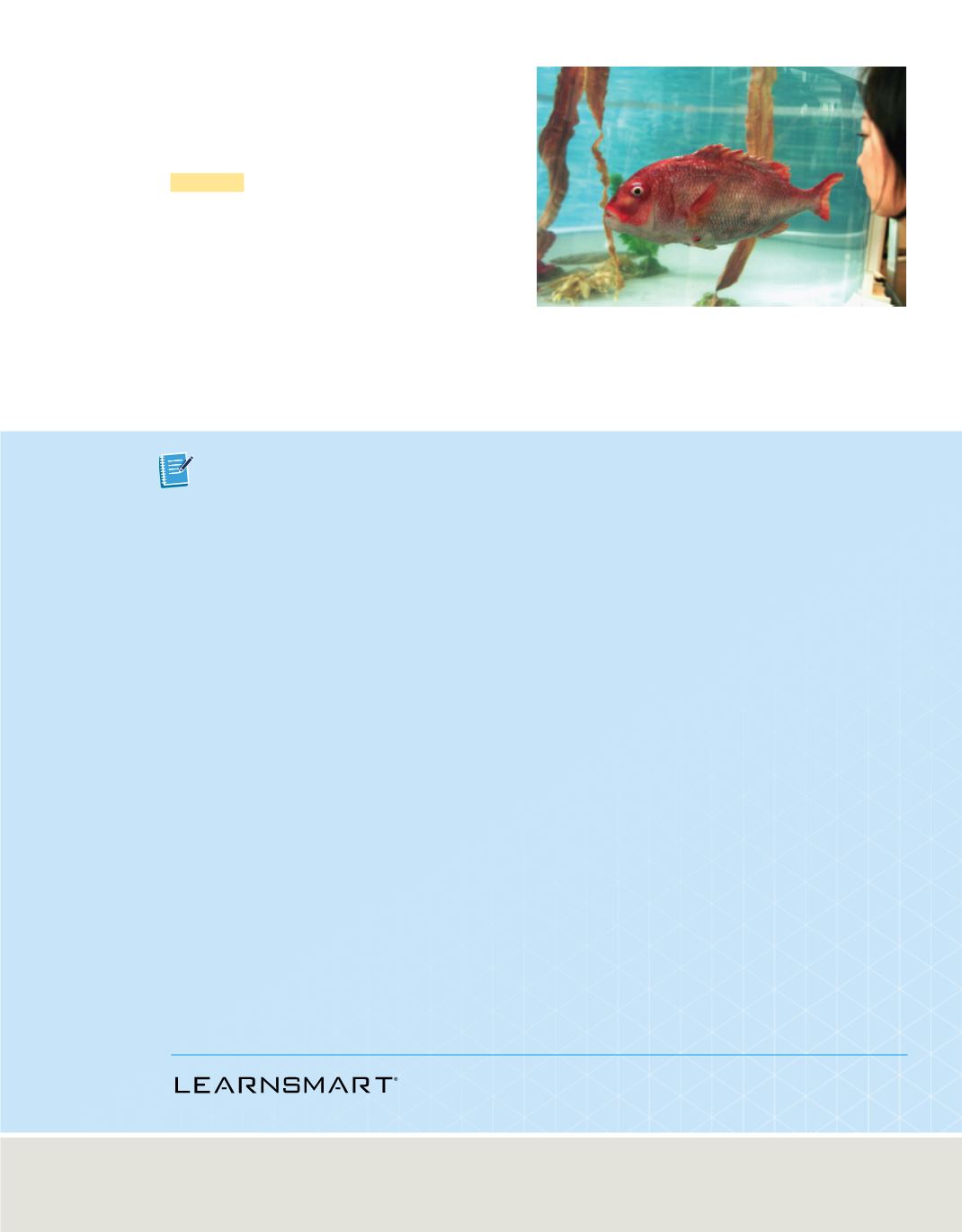
Figure 7
Scientists developing submarine technology created
this robot that looks and swims like a real fish. Its body is
made of a silicon resin that softens in water.
Metalloids
The elements in the green boxes bordering
the stairstep line in
Figure 4
are called metalloids,
or semimetals.
Metalloids
have physical and chemical properties
of both metals and nonmetals. Silicon (Si) and
germanium (Ge) are two important metalloids
used extensively in computer chips and solar cells.
Silicon is also used to make prosthetics or in
lifelike applications, as shown in
Figure 7
.
This introduction to the periodic table touches
only the surface of its durable explanatory
power. You can refer to the Elements Hand-
book at the end of your textbook to learn more
about the elements and their various groups.
Lesson 1 • Development of the Modern Periodic Table
145









