
Go online to follow your personalized learning path to review, practice,
and reinforce your understanding.
Summary
• The radioactive decay of
unstable nuclei involves the
release of energy.
• There are three types of
radiation: alpha (charge of 2
+
),
beta (charge of 1
-
) and gamma
(no charge).
• The neutron-to-proton ratio of
an atom’s nucleus determines
its stability.
Demonstrate Understanding
24.
Describe
the difference between radioactivity and
radioactive decay.
25.
State
what quantities are conserved and which are
not conserved in a nuclear reaction.
26.
Explain
why beta particles are deflected towards a
positive plate, alpha particles are deflected towards a
negative plate, and gamma rays are not deflected.
27.
Calculate
How much more mass does an alpha
particle have compared to an electron?
28.
Create
a table showing how each type of radiation
affects the atomic number and mass number of an
atom.
Check Your Progress
Gamma radiation
The third common
type of radiation is called gamma
radiation, or gamma rays. A
gamma ray
is
high-energy radiation that has no mass
and is denoted by the symbol γ. Gamma
rays are neutral, and so are not deflected
by electric or magnetic fields. They often
accompany alpha and beta radiation, and
account for most of the energy lost during
radioactive decay. For example, gamma
rays accompany the decay of uranium-238.
238
92
U
→
234
90
Th
+
α
+
2
γ
uranium-238 thorium-234 alpha particle gamma rays
Because gamma rays are massless, the emission of gamma rays by themselves cannot
result in the formation of a new element.
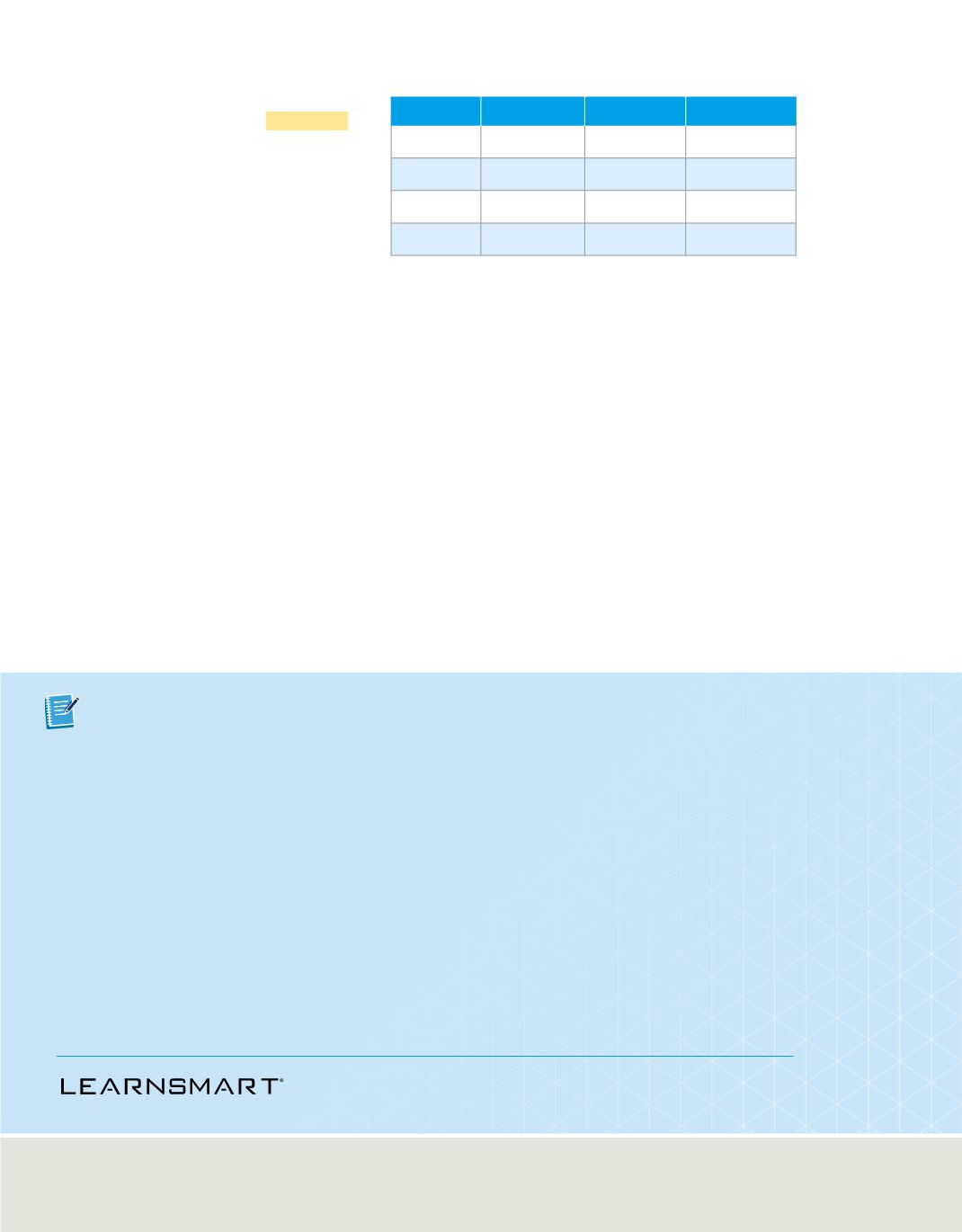
Table 5
summarizes the characteristics of
alpha, beta, and gamma radiation.
Nuclear stability
Much of science deals with understanding how things change and
how they remain stable. An atom’s stability is governed by its ratio of neutrons to
protons. Atoms that contain either too many or too few neutrons are unstable and lose
energy as they decay to form a stable nucleus. They emit alpha and beta particles, which
affect the neutron-to-proton ratio of the newly created nucleus. Eventually, radioactive
atoms undergo enough radioactive decay to form stable, nonradioactive atoms.
Table 5
Characteristics of Radiation
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
Symbol
4
2
He or
α
e
-
or
β
γ
Mass (amu)
4
1 ____ 1840
0
Mass (kg)
6.65
×
10
–27
9.11
×
10
–31
0
Charge
2
+
1
-
0
100
Module 3 • The Structure of the Atom









