
(l)Glow Images, (r)Wlad74/Shutterstock.com
Copper wires
Figure 7
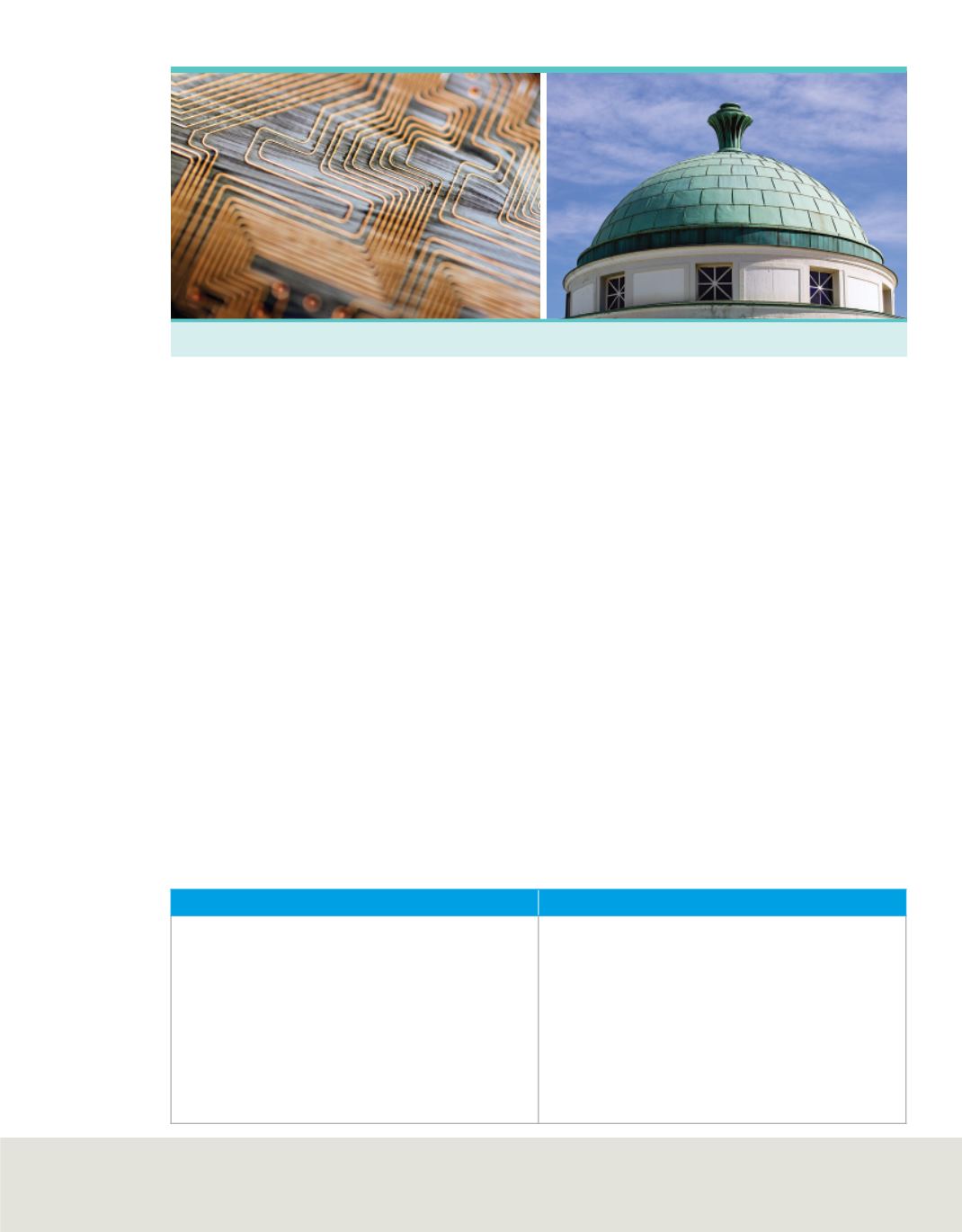
One of the physical properties of copper is that it can be shaped into different forms, such as the
wires on circuit boards. The fact that copper turns from reddish to green when reacting with substances in
the air is a chemical property.
Observing Properties of Matter
Every substance has its own unique set of physical and chemical properties.
Figure 7
shows physical and chemical properties of copper. Copper can be shaped into different
forms, which is a physical property. When copper is in contact with air for a long time,
it reacts with the substances in the air and turns green. This is a chemical property.
Table 2
lists several physical and chemical properties of copper.
Properties and states of matter
The properties of copper listed in
Table 2
might vary depending on the conditions
under which they are observed. Because the particular form, or state, of a substance is a
physical property, changing the state introduces or adds another physical property to its
characteristics. It is important to state the specific conditions, such as temperature and
pressure, under which observations are made because both physical and chemical
properties depend on these conditions. Resources that provide tables of physical and
chemical properties of substances, such as the
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics,
generally include the physical properties of substances in all of the states in which they
can exist.
Table 2
Properties of Copper
Physical Properties
Chemical Properties
• reddish brown, shiny
• easily shaped into sheets (malleable) and drawn
into wires (ductile)
• a good conductor of heat and electricity
• density
=
8.96 g/cm
3
• melting point
=
1085°C
• boiling point
=
2562°C
• forms green copper carbonate compound when
in contact with moist air
• reacts with nitric acid and sulfuric acid, forming
new substances
• one type of compound forms a deep-blue solution
when in contact with ammonia
Copper roof
Lesson 1 • Properties of Matter
53









