
C03_006A
Solid
McGraw-Hill Education
Figure 2
A solid has a definite shape and does not take the shape of its container. Particles in a solid are
tightly packed.
Recall that matter with a uniform and unchanging composition is called a substance,
also known as a pure substance. Table salt is a pure substance. Another example of a
pure substance is pure water. Water is always composed of hydrogen and oxygen.
Seawater and tap water, on the other hand, are not pure substances because samples
taken from different locations will often have different compositions. That is, the
samples will contain different amounts of water, minerals, and other dissolved
substances. Substances are important; much of your chemistry course will be focused
on the composition of substances and how they interact with one another.
States of Matter
Imagine you are sitting on a sunny bench, breathing heavily and drinking water after
playing a game of soccer. You are interacting with four different forms of matter—the
bench is a solid, the water is a liquid, the air you breathe is a gas, and the Sun is a plasma.
Although scientists recognize other forms, matter that exists naturally on Earth can be
classified as one of these physical forms, which are called
states of matter.
Each state of
matter can be distinguished by its properties.
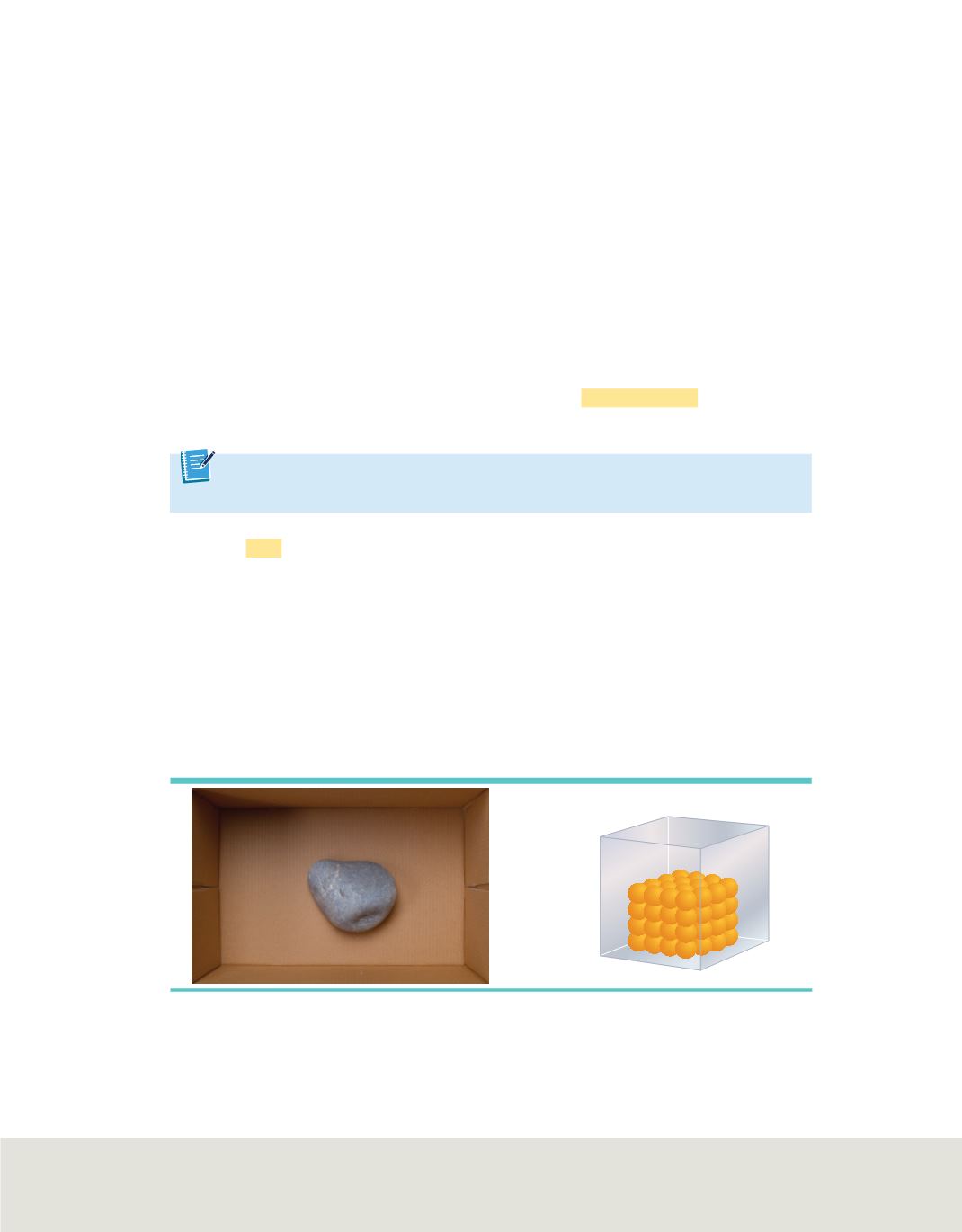
Solids
A
solid
is a form of matter that has its own definite shape and volume. Wood,
iron, paper, and sugar are all examples of solids. The particles of matter in a solid are
tightly packed. When heated, a solid expands, but only slightly. Because its shape is
definite, a solid might not conform to the shape of the container in which it is placed. If
you place a rock into a container, the rock will not take the shape of the container, as
shown in
Figure 2
. The tight packing of particles in a solid makes it incompressible;
that is, it cannot be pressed into a smaller volume. It is important to understand that a
solid is not defined by its rigidity or hardness. For instance, although concrete is rigid
and wax is soft, they are both solids.
Get It?
Name
four states of matter.
Lesson 1 • Properties of Matter
49









