
Science & Society Picture Library/Getty Images
Figure 2
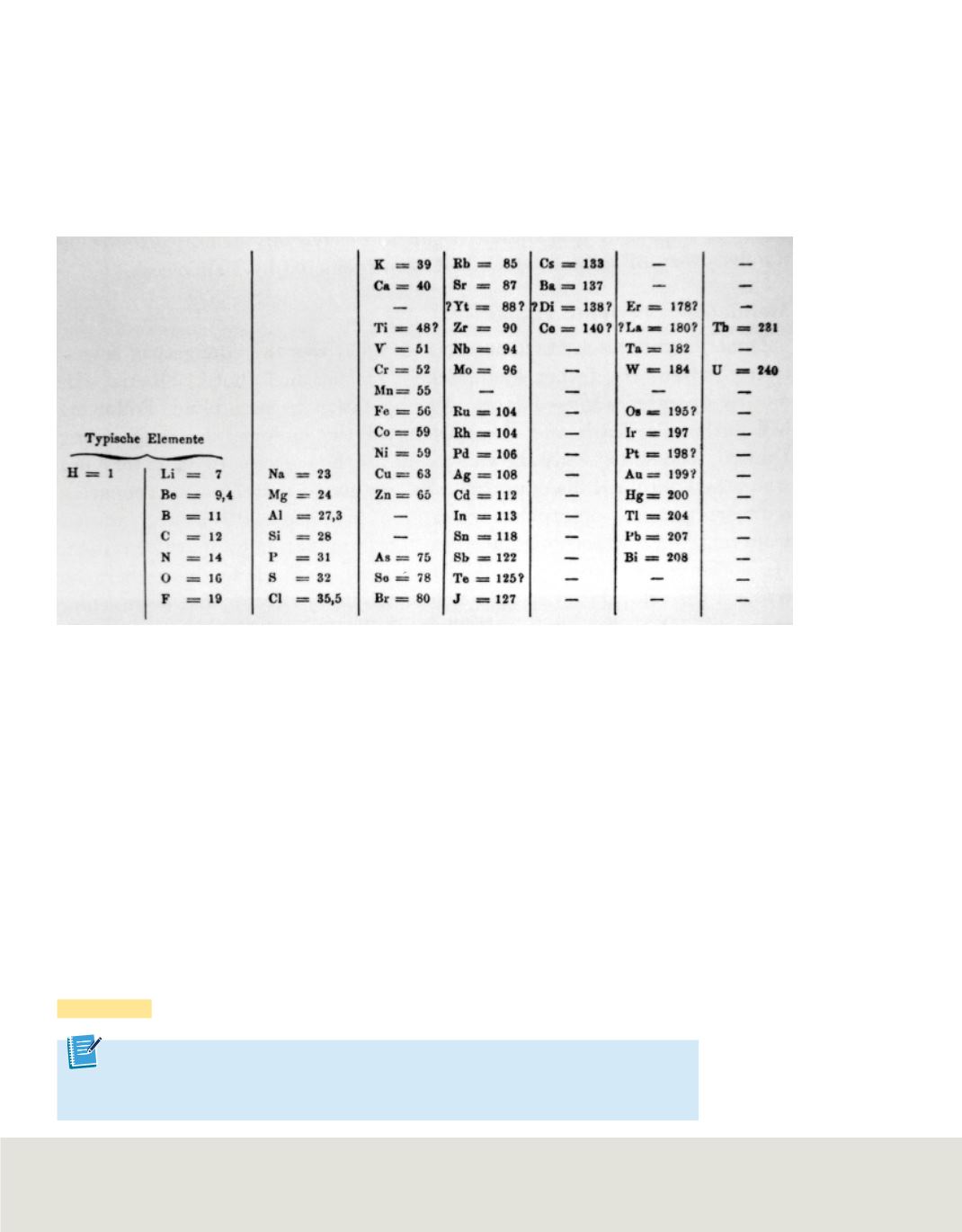
In the first version of his table, published in 1869, Mendeleev arranged elements with similar
chemical properties horizontally. He left empty spaces for elements that were not yet discovered.
Get It?
Compare and contrast
the ways in which Mendeleev and Moseley organized the
elements.
By arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic mass into columns with similar
properties, Mendeleev organized the elements into a periodic table.
Mendeleev’s table, shown in
Figure 2
, became widely accepted because he predicted the
existence and properties of undiscovered elements that were later found. Mendeleev
left blank spaces in the table where he thought the undiscovered elements should go.
By noting trends in the properties of known elements, he was able to predict the
properties of the yet-to-be-discovered elements scandium, gallium, and germanium.
Moseley
Mendeleev’s table, however, was not completely correct. After several new elements
were discovered and the atomic masses of the known elements were more accurately
determined, it became apparent that several elements in his table were not in the
correct order. Arranging the elements by mass resulted in several elements being placed
in groups of elements with differing properties. The reason for this problem was deter-
mined in 1913 by English chemist Henry Moseley (1887–1915). Moseley discovered that
atoms of each element contain a unique number of protons in their nuclei—the number
of protons being equal to the atom’s atomic number. By arranging the elements in order
of increasing atomic number, the problems with the order of the elements in the peri-
odic table were solved and a clear periodic pattern of properties resulted.
The statement that there is a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of
the elements when they are arranged by increasing atomic number is called the
periodic law.
140
Module 5 • The Periodic Table and Periodic Law









