
The naturally-occurring elements are not equally abundant. For example, hydrogen is
estimated to make up approximately 75% of the mass of the universe. Oxygen and
silicon together comprise almost 75% of the mass of Earth’s crust, while oxygen, carbon,
and hydrogen account for more than 90% of the human body. Francium, on the other
hand, is one of the least-abundant naturally-occurring elements. There is probably less
than 20 g of francium dispersed throughout Earth’s crust.
A first look at the periodic table
As many new elements were being discovered
in the early nineteenth century, chemists began to observe and study patterns of
similarities in the chemical and physical properties of particular sets of elements. In
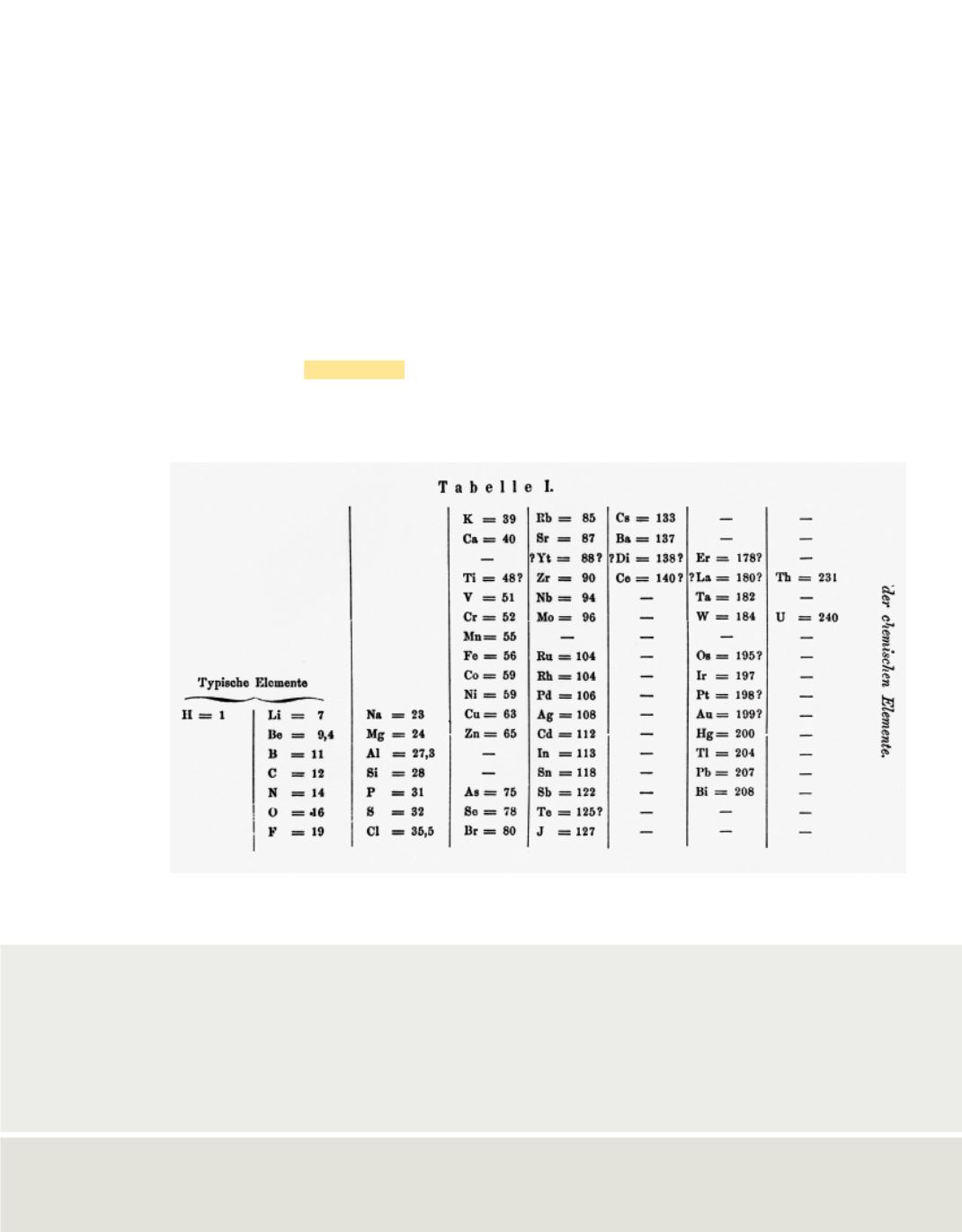
1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834–1907) devised a chart, shown in
Figure 14
, which organized all of the elements that were known at the time. His
classification was based on the similarities and masses of the elements. Mendeleev’s
table was the first version of what has been further developed into the periodic table of
the elements. The
periodic table
organizes the elements into a grid of horizontal rows
called periods and vertical columns called groups or families. Elements in the same
group have similar chemical and physical properties. The table is called periodic
because the pattern of similar properties repeats from period to period.
Figure 14
Mendeleev was one of the first scientists to organize elements in a periodic manner, as shown in
this chart, and to observe periodic patterns in the properties of the elements.
SCIENCE USAGE V. COMMON USAGE
element
Science usage:
a pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler
substances by ordinary chemical means
Lead is one of the heaviest elements.
Common usage:
the state or sphere that is natural or suited to any person or thing
In snow, huskies are in their element.
Lesson 3 • Elements and Compounds
61
Science & Society Picture Library/Getty Images









